Difference between revisions of "OpenVPN Routed"
Unnilennium (talk | contribs) |
m (→Requirements) |
||
| (34 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Languages}} | {{Languages}} | ||
| − | + | {{usefulnote}} | |
| + | <blockquote style="float: right;">[[File:openvpn.png|250px]]</blockquote><br> | ||
===Maintainer=== | ===Maintainer=== | ||
| − | [mailto:daniel@firewall-services.com[[User:VIP-ire|Daniel B. | + | [mailto:daniel@firewall-services.com][[User:VIP-ire|Daniel B.]] from [http://www.firewall-services.com Firewall Services] |
| − | === Version === | + | ===Version=== |
| − | {{ #smeversion: smeserver-openvpn-routed}} | + | {{#smeversion: smeserver-openvpn-routed }} |
=== Description === | === Description === | ||
| Line 13: | Line 14: | ||
[http://openvpn.net OpenVPN] is a full-featured open source SSL VPN solution that accommodates a wide range of configurations, including remote access, site-to-site VPNs, Wi-Fi security, and enterprise-scale remote access solutions with load balancing, fail-over, and fine-grained access-controls. Starting with the fundamental premise that complexity is the enemy of security, OpenVPN offers a cost-effective, lightweight alternative to other VPN technologies that is well-targeted for the SME and enterprise markets. | [http://openvpn.net OpenVPN] is a full-featured open source SSL VPN solution that accommodates a wide range of configurations, including remote access, site-to-site VPNs, Wi-Fi security, and enterprise-scale remote access solutions with load balancing, fail-over, and fine-grained access-controls. Starting with the fundamental premise that complexity is the enemy of security, OpenVPN offers a cost-effective, lightweight alternative to other VPN technologies that is well-targeted for the SME and enterprise markets. | ||
| − | This contrib will help you configuring OpenVPN in | + | This contrib will help you configuring '''OpenVPN in routed mode'''. With this mode, clients connecting to the VPN from the outside will get an IP in a virtual private network. (this network will use a '''separated IP range''' from your standard local network, unlike the [[OpenVPN_Bridge]] contrib |
=== Requirements === | === Requirements === | ||
| − | *SME Server | + | *SME Server 9.0+ (serveronly or server&gateway works) |
| − | |||
*You may want to install [[PHPki]] to manage easily your certificates. | *You may want to install [[PHPki]] to manage easily your certificates. | ||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
=== Installation === | === Installation === | ||
| + | <tabs container><tab name="For SME 10"> | ||
| + | /!\ new default cipher = AES-128-GCM and HMAC SHA256, if you have issues check the configuration options | ||
| + | yum install smeserver-openvpn-routed --enablerepo=smecontribs | ||
| + | if you have smeserver-openvpn-bridge installed and configured then all will work automaticly. | ||
| + | It will change its port to a different one, and it will copy certificates from the bridge openvpn | ||
| − | + | to know the new port | |
| + | config getprop openvpn-routed UDPPort | ||
| + | </tab> | ||
| + | <tab name="For SME 9"> | ||
install fws repo, see : [[Fws]] | install fws repo, see : [[Fws]] | ||
| Line 33: | Line 41: | ||
yum install smeserver-openvpn-routed --enablerepo=fws,smecontribs | yum install smeserver-openvpn-routed --enablerepo=fws,smecontribs | ||
| − | + | you will then have to configure by hand | |
| + | |||
| + | If you already run the [[OpenVPN_Bridge]] contrib, you can just copy all the certificates: | ||
| + | cp -a /etc/openvpn/bridge/{priv,pub} /etc/openvpn/routed/ | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | </tab> | ||
| + | </tabs> | ||
| + | === Configure === | ||
| + | |||
| + | This contribs is really minimal and doesn't have a panel to configure everything. You have to configure all by hand. Except on SME10 if you already have smeserver-openvpn-bridge installed and configured. | ||
| + | |||
| + | here's the file the contrib expects to see before being started: | ||
| + | |||
| + | * /etc/openvpn/routed/pub/cert.pem (the server certificate, in PEM format) | ||
| + | * /etc/openvpn/routed/pub/cacert.pem (the CA certificate, in PEM format) | ||
| + | * /etc/openvpn/routed/pub/dh.pem (Diffie-Helman parameters) | ||
| + | * /etc/openvpn/routed/priv/key.pem (the server private key) | ||
| + | * /etc/openvpn/routed/priv/takey.pem (an optional shared key) | ||
| + | |||
| + | and an available port to bind to. | ||
| + | |||
| − | + | ==== Using PHPki ==== | |
| + | If you are using the PHPki contrib to manage your certificates you need to do the following : | ||
| + | Create a new certificate for your OpenVPN server - make sure it is a VPN server only certificate. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Note box|Make sure you don't protect the private key with a password}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | From PHPki get the following certificates : | ||
| + | |||
| + | From the main page of PHPki : | ||
| + | |||
| + | dh pub/dh.pem - Download the Diffie-Hellman parameters | ||
| + | ca pub/cacert.pem - Download the Root Certificate | ||
| + | |||
| + | If you need to, get a copy of the revocation list | ||
| + | crl-verify pub/cacrl.pem - Download the Certificate Revocation List | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Revocation certificate can be obtained automatically with a cronjob | ||
| + | db configuration setprop openvpn-routed CrlUrl 'https://your-phpki-box.domain.net/phpki/index.php?stage=dl_crl_pem' | ||
| + | |||
| + | From the Manage Certificates page of PHPki : | ||
| + | |||
| + | cert pub/cert.pem - use the PEM Certificate | ||
| + | key priv/key.pem - use the PEM Key | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Copy them to the relevant directories as above | ||
| + | |||
| + | Make sure that the certs are set 0600 | ||
| + | |||
| + | If you want your VPN clients to use the SME as default gateway for all traffic once connected : | ||
| + | |||
| + | db configuration setprop openvpn-routed RedirectGateway enabled | ||
| + | signal-event openvpn-routed-update | ||
| + | |||
| + | You can now add your Client certificates to your device. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Make sure you have a user on the server. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Make sure in your device that you choose Certificate + Password as an option. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Enter in your user name and password in addition to the certificates | ||
==== Configure as running in parallel of bridge contrib ==== | ==== Configure as running in parallel of bridge contrib ==== | ||
| + | Not needed for SME10, the contrib does it for you. | ||
#install | #install | ||
| Line 46: | Line 116: | ||
#copy bridge certificates | #copy bridge certificates | ||
cp -a /etc/openvpn/bridge/{priv,pub} /etc/openvpn/routed/ | cp -a /etc/openvpn/bridge/{priv,pub} /etc/openvpn/routed/ | ||
| − | # if you want to | + | # if you want to change the default network range assigned (192.169.29.0) |
| − | db configuration setprop openvpn-routed | + | db configuration setprop openvpn-routed Network 192.168.79.0/255.255.255.0 |
# signale event to regenerate all you need | # signale event to regenerate all you need | ||
signal-event openvpn-routed-update | signal-event openvpn-routed-update | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Client configuration - iOS=== | ||
| + | You can connect using the free [https://itunes.apple.com/us/app/openvpn-connect/id590379981?mt=8 OpenVPN Connect] app. Unfortunately, configuring this app for your connection is a somewhat involved process. It will require creating or downloading a PKCS#12 file manually for the client, creating a .ovpn configuration file, installing the CA and client certificates on your iOS device, and finally importing the .ovpn configuration file into your device. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Create a PKCS#12 file for the client==== | ||
| + | A PKCS#12 file is used to bundle the client's private key with its associated certificates, and will be used to install an identity on your iOS device. [[PHPki|PHPki]] has the ability to generate these files for download, but does not require a password for the client certificate if you have chosen the role of VPN client only when creating the certificate. iOS, however, requires a password to import a PKCS#12 file. If you entered a password when you created the client certificate, you can simply download the .p12 file from PHPki and import it using the instructions below. If you did not enter a password, you will need to create the PKCS#12 file manually. Begin by using PHPki to download a PEM bundle for the client. Log into the server-manager, go to Certificate Management, then to Manage Certificates, and click the download icon to the right of the client certificate you want to use. On the next screen, in the file type dropdown, choose PEM Bundle w/Root. Save this file to a convenient location and open it with your favorite text editor. It will look like this: | ||
| + | |||
| + | -----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY----- | ||
| + | MIIEwAIBADANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAASCBKowggSmAgEAAoIBAQDhKd2tv7D6lnzs | ||
| + | ... | ||
| + | P9sSy5mmpaI3o+vRt6fXYCvL37g= | ||
| + | -----END PRIVATE KEY----- | ||
| + | -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- | ||
| + | MIIGuzCCBKOgAwIBAgIDEAACMA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBBQUAMIHLMQswCQYDVQQGEwJV | ||
| + | ... | ||
| + | ex7wHUDqk6zpdeygiuK8fYAbbeb7/9EGopKOPI8J+PPyaJ96ljqDK6FphY3Jt0k= | ||
| + | -----END CERTIFICATE----- | ||
| + | -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- | ||
| + | MIIHWjCCBUKgAwIBAgIJAPM30y+H/VCKMA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBBQUAMIHLMQswCQYD | ||
| + | ... | ||
| + | Wx8wzFUHXwxOlYGsDRK9r/NTlPyiKwV9Z/kxVFSrFR7/FwCu8Ty4dSmsENk7xEzh | ||
| + | wAhb0RNq1QLkr/0K6KQ= | ||
| + | -----END CERTIFICATE----- | ||
| + | |||
| + | The first block is the client's private key, the second block is the client's certificate, and the third block is the CA certificate. You'll need to split these out into three files. Name them, for the sake of clarity, user.key, user.crt, and ca.crt. Save these three files in a location that's accessible to your SME server. Then you can actually create the PKCS#12 file using this command: | ||
| + | $ openssl pkcs12 -export -in user.crt -inkey user.key -certfile ca.crt -name MyClient -out client.p12 | ||
| + | |||
| + | You may replace MyClient with whatever client name you wish. In processing this, openssl will ask for a password; you must enter one. When the system returns to the shell prompt, your client.p12 file will be ready to use. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Create .ovpn configuration file==== | ||
| + | The .ovpn configuration file tells the OpenVPN Connect client how to connect to your server. Begin by logging into the server-manager and going to OpenVPN-Bridge on the left sidebar. Click the button marked "Display a functional client configuration file." Copy the text that's shown into your favorite text editor and save it as client.ovpn. You'll then need to make some changes. | ||
| + | |||
| + | First, remove the first two lines. Second, on the first remaining line, change "dev tap" to "dev tun". This is required for iOS compatibility. Third, comment out or remove the line that says "pkcs12 user.p12". Third, change the line that says "remote" to read "remote yourserver.tld 1195 udp". Finally, add your CA certificate to the end of the file, like this: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <ca> | ||
| + | -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- | ||
| + | MIIHWjCCBUKgAwIBAgIJAPM30y+H/VCKMA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBBQUAMIHLMQswCQYD | ||
| + | VQQGEwJVUzEXMBUGA1UECBMOU291dGggQ2Fyb2xpbmExEzARBgNVBAcTCkhhcnRz | ||
| + | ... | ||
| + | Wx8wzFUHXwxOlYGsDRK9r/NTlPyiKwV9Z/kxVFSrFR7/FwCu8Ty4dSmsENk7xEzh | ||
| + | wAhb0RNq1QLkr/0K6KQ= | ||
| + | -----END CERTIFICATE----- | ||
| + | </ca> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Save this file. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Install CA and client certificates on your iOS device==== | ||
| + | Email the ca.crt and client.p12 files to an account that your iOS device can reach using the built-in Mail app. Using the Mail app, open the message and tap on the ca.crt file to open it. The device will take you through the steps of installing the file, and once it is installed, will return you to the message. Then tap on the client.p12 file and follow the prompts to install it, including entering the password. Again, once it is installed, you'll be returned to the email message. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Importing .ovpn file and configuring connection==== | ||
| + | To configure the OpenVPN Connect app, you'll need to copy the .ovpn file to your device using iTunes. Open iTunes, select your device, and choose Apps from the left sidebar. In the right-hand frame, scroll down to the heading "The apps listed below can transfer documents between your iPhone and this computer". Under that heading, scroll down in the apps list and click on OpenVPN. Drag and drop the .ovpn file to the right-hand frame, under the heading "OpenVPN Documents." | ||
| + | [[File:Itunes_transfer_ovpn.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | This will take a moment to sync. Once that is completed, open the OpenVPN Connect app on your device. It will inform you that there's a new profile available for import. On that screen, tap the green + button. | ||
| + | [[File:Openvpn_newprofile.PNG]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | The app will open the profile and indicate that it isn't associated with an identity by showing "None selected". Tap where it says "None selected" to choose an identity profile. | ||
| + | [[File:Openvpn_importprofile.PNG]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Next, the app will list your available identity profiles. Choose the one you want to associate with this OpenVPN connection. | ||
| + | [[File:Openvpn_chooseidentity.PNG]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Configuration is now complete. You can connect to your OpenVPN server using the slider on the screen. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Default key properties === | ||
| + | these properties can be modified simply by issuing | ||
| + | |||
| + | config setprop openvpn-routed ''property'' ''newvalue'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | to reset to default, simply issue: | ||
| + | config delprop openvpn-routed ''property'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | where you have to replace ''property'' and ''newvalue'' with what you want. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! db !! Key !! Type !! Property !! Default !! Allowed !! Description | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | configuration || openvpn-routed || service || || || || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | || || || Protocol || udp || udp / tcp || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | || || || UDPPort || 1194 || || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | || || || TCPPort || 1194 || || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | || || || Authentication || CrtWithPass || || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | || || || Network || 192.168.29.0/255.255.255.0 || user defined || | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | || || || PushLocalNetworks || enabled || enabled / disabled || | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | || || || RedirectGateway || disabled || enabled / disabled || | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | || || || Mtu || none || [nnnn] || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | || || || Fragment || none || || | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | || || || DuplicateCN || disabled || enabled / disabled || | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | || || || PassTOS || enabled || enabled / disabled || | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | || || || Compression || enabled || enabled / disabled || | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | || || || MaxClients || none || 1 - 254 || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | || || || ConfigRequired || disabled || enabled / disabled || | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | || || || Verbose || 3 || [n] || | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | || || || Cipher || None || Various. AES-128-CBC || Default BF-CBC deprecated | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | || || || HMAC || None || Various. SHA256 || Default SHA1 deprecated | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | || || || CrlUrl ||None || http://url/phpki/index.php?stage=dl_crl_pem || | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | you can also set the property PushRoute to disabled to any network in networks db to avoid the contrib to push the network to the client | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Workarounds and known issues=== | ||
| + | if you migrate from SME8 to SME9 and are not able to connect after correctly migrating your certificates, this might be related to not secure enough algorithm. CentOS 6.9 release notes state that "Support for insecure cryptographic protocols and algorithms has been dropped. This affects usage of MD5, SHA0, RC4 and DH parameters shorter than 1024 bits." Of course real solution would be to migrate all your certs to better algorithm. | ||
| + | |||
| + | workaround :<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| + | echo -e "LegacySigningMDs md2 md5\nMinimumDHBits 512\n" >> /etc/pki/tls/legacy-settings | ||
| + | service openvpn-routed restart | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Bugs=== | ||
| + | Please raise bugs under the SME-Contribs section in [http://bugs.contribs.org/enter_bug.cgi bugzilla] | ||
| + | and select the smeserver-openvpn-routed component or use {{BugzillaFileBug|product=SME%20Contribs|component=smeserver-openvpn-routed|title=this link}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {{#bugzilla:columns=id,product,version,status,summary |sort=id |order=desc |component=smeserver-openvpn-routed|noresultsmessage="No open bugs found."}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Changelog=== | ||
| + | Only versions released in smecontrib are listed here. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{#smechangelog: smeserver-openvpn-routed}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Other articles in this category== | ||
| + | {{#ask: [[Category:VPN]]}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Contrib]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Administration:VPN]] | ||
| + | [[Category:VPN]] | ||
Latest revision as of 18:06, 3 January 2025
Is this article helpful to you?
Please consider donating or volunteering
Thank you!
Maintainer
[1]Daniel B. from Firewall Services
Version
Description
OpenVPN is a full-featured open source SSL VPN solution that accommodates a wide range of configurations, including remote access, site-to-site VPNs, Wi-Fi security, and enterprise-scale remote access solutions with load balancing, fail-over, and fine-grained access-controls. Starting with the fundamental premise that complexity is the enemy of security, OpenVPN offers a cost-effective, lightweight alternative to other VPN technologies that is well-targeted for the SME and enterprise markets.
This contrib will help you configuring OpenVPN in routed mode. With this mode, clients connecting to the VPN from the outside will get an IP in a virtual private network. (this network will use a separated IP range from your standard local network, unlike the OpenVPN_Bridge contrib
Requirements
- SME Server 9.0+ (serveronly or server&gateway works)
- You may want to install PHPki to manage easily your certificates.
Installation
/!\ new default cipher = AES-128-GCM and HMAC SHA256, if you have issues check the configuration options
yum install smeserver-openvpn-routed --enablerepo=smecontribs
if you have smeserver-openvpn-bridge installed and configured then all will work automaticly. It will change its port to a different one, and it will copy certificates from the bridge openvpn
to know the new port
config getprop openvpn-routed UDPPort
install fws repo, see : Fws
then :
yum install smeserver-openvpn-routed --enablerepo=fws,smecontribs
you will then have to configure by hand
If you already run the OpenVPN_Bridge contrib, you can just copy all the certificates:
cp -a /etc/openvpn/bridge/{priv,pub} /etc/openvpn/routed/
Configure
This contribs is really minimal and doesn't have a panel to configure everything. You have to configure all by hand. Except on SME10 if you already have smeserver-openvpn-bridge installed and configured.
here's the file the contrib expects to see before being started:
- /etc/openvpn/routed/pub/cert.pem (the server certificate, in PEM format)
- /etc/openvpn/routed/pub/cacert.pem (the CA certificate, in PEM format)
- /etc/openvpn/routed/pub/dh.pem (Diffie-Helman parameters)
- /etc/openvpn/routed/priv/key.pem (the server private key)
- /etc/openvpn/routed/priv/takey.pem (an optional shared key)
and an available port to bind to.
Using PHPki
If you are using the PHPki contrib to manage your certificates you need to do the following :
Create a new certificate for your OpenVPN server - make sure it is a VPN server only certificate.
From PHPki get the following certificates :
From the main page of PHPki :
dh pub/dh.pem - Download the Diffie-Hellman parameters ca pub/cacert.pem - Download the Root Certificate
If you need to, get a copy of the revocation list
crl-verify pub/cacrl.pem - Download the Certificate Revocation List
The Revocation certificate can be obtained automatically with a cronjob
db configuration setprop openvpn-routed CrlUrl 'https://your-phpki-box.domain.net/phpki/index.php?stage=dl_crl_pem'
From the Manage Certificates page of PHPki :
cert pub/cert.pem - use the PEM Certificate key priv/key.pem - use the PEM Key
Copy them to the relevant directories as above
Make sure that the certs are set 0600
If you want your VPN clients to use the SME as default gateway for all traffic once connected :
db configuration setprop openvpn-routed RedirectGateway enabled signal-event openvpn-routed-update
You can now add your Client certificates to your device.
Make sure you have a user on the server.
Make sure in your device that you choose Certificate + Password as an option.
Enter in your user name and password in addition to the certificates
Configure as running in parallel of bridge contrib
Not needed for SME10, the contrib does it for you.
- install
- change port
config setprop openvpn-routed UDPPort 1195
- copy bridge certificates
cp -a /etc/openvpn/bridge/{priv,pub} /etc/openvpn/routed/
- if you want to change the default network range assigned (192.169.29.0)
db configuration setprop openvpn-routed Network 192.168.79.0/255.255.255.0
- signale event to regenerate all you need
signal-event openvpn-routed-update
Client configuration - iOS
You can connect using the free OpenVPN Connect app. Unfortunately, configuring this app for your connection is a somewhat involved process. It will require creating or downloading a PKCS#12 file manually for the client, creating a .ovpn configuration file, installing the CA and client certificates on your iOS device, and finally importing the .ovpn configuration file into your device.
Create a PKCS#12 file for the client
A PKCS#12 file is used to bundle the client's private key with its associated certificates, and will be used to install an identity on your iOS device. PHPki has the ability to generate these files for download, but does not require a password for the client certificate if you have chosen the role of VPN client only when creating the certificate. iOS, however, requires a password to import a PKCS#12 file. If you entered a password when you created the client certificate, you can simply download the .p12 file from PHPki and import it using the instructions below. If you did not enter a password, you will need to create the PKCS#12 file manually. Begin by using PHPki to download a PEM bundle for the client. Log into the server-manager, go to Certificate Management, then to Manage Certificates, and click the download icon to the right of the client certificate you want to use. On the next screen, in the file type dropdown, choose PEM Bundle w/Root. Save this file to a convenient location and open it with your favorite text editor. It will look like this:
-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY----- MIIEwAIBADANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAASCBKowggSmAgEAAoIBAQDhKd2tv7D6lnzs ... P9sSy5mmpaI3o+vRt6fXYCvL37g= -----END PRIVATE KEY----- -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- MIIGuzCCBKOgAwIBAgIDEAACMA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBBQUAMIHLMQswCQYDVQQGEwJV ... ex7wHUDqk6zpdeygiuK8fYAbbeb7/9EGopKOPI8J+PPyaJ96ljqDK6FphY3Jt0k= -----END CERTIFICATE----- -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- MIIHWjCCBUKgAwIBAgIJAPM30y+H/VCKMA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBBQUAMIHLMQswCQYD ... Wx8wzFUHXwxOlYGsDRK9r/NTlPyiKwV9Z/kxVFSrFR7/FwCu8Ty4dSmsENk7xEzh wAhb0RNq1QLkr/0K6KQ= -----END CERTIFICATE-----
The first block is the client's private key, the second block is the client's certificate, and the third block is the CA certificate. You'll need to split these out into three files. Name them, for the sake of clarity, user.key, user.crt, and ca.crt. Save these three files in a location that's accessible to your SME server. Then you can actually create the PKCS#12 file using this command:
$ openssl pkcs12 -export -in user.crt -inkey user.key -certfile ca.crt -name MyClient -out client.p12
You may replace MyClient with whatever client name you wish. In processing this, openssl will ask for a password; you must enter one. When the system returns to the shell prompt, your client.p12 file will be ready to use.
Create .ovpn configuration file
The .ovpn configuration file tells the OpenVPN Connect client how to connect to your server. Begin by logging into the server-manager and going to OpenVPN-Bridge on the left sidebar. Click the button marked "Display a functional client configuration file." Copy the text that's shown into your favorite text editor and save it as client.ovpn. You'll then need to make some changes.
First, remove the first two lines. Second, on the first remaining line, change "dev tap" to "dev tun". This is required for iOS compatibility. Third, comment out or remove the line that says "pkcs12 user.p12". Third, change the line that says "remote" to read "remote yourserver.tld 1195 udp". Finally, add your CA certificate to the end of the file, like this:
<ca> -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- MIIHWjCCBUKgAwIBAgIJAPM30y+H/VCKMA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBBQUAMIHLMQswCQYD VQQGEwJVUzEXMBUGA1UECBMOU291dGggQ2Fyb2xpbmExEzARBgNVBAcTCkhhcnRz ... Wx8wzFUHXwxOlYGsDRK9r/NTlPyiKwV9Z/kxVFSrFR7/FwCu8Ty4dSmsENk7xEzh wAhb0RNq1QLkr/0K6KQ= -----END CERTIFICATE----- </ca>
Save this file.
Install CA and client certificates on your iOS device
Email the ca.crt and client.p12 files to an account that your iOS device can reach using the built-in Mail app. Using the Mail app, open the message and tap on the ca.crt file to open it. The device will take you through the steps of installing the file, and once it is installed, will return you to the message. Then tap on the client.p12 file and follow the prompts to install it, including entering the password. Again, once it is installed, you'll be returned to the email message.
Importing .ovpn file and configuring connection
To configure the OpenVPN Connect app, you'll need to copy the .ovpn file to your device using iTunes. Open iTunes, select your device, and choose Apps from the left sidebar. In the right-hand frame, scroll down to the heading "The apps listed below can transfer documents between your iPhone and this computer". Under that heading, scroll down in the apps list and click on OpenVPN. Drag and drop the .ovpn file to the right-hand frame, under the heading "OpenVPN Documents."
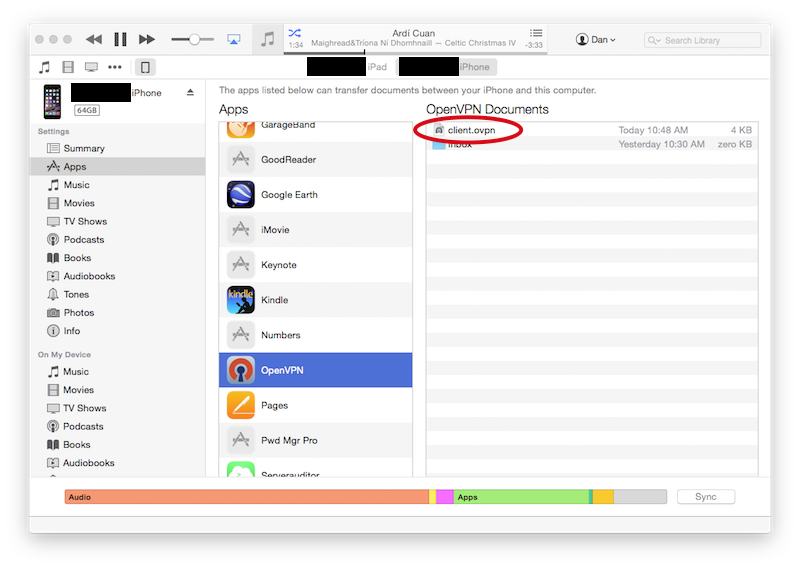
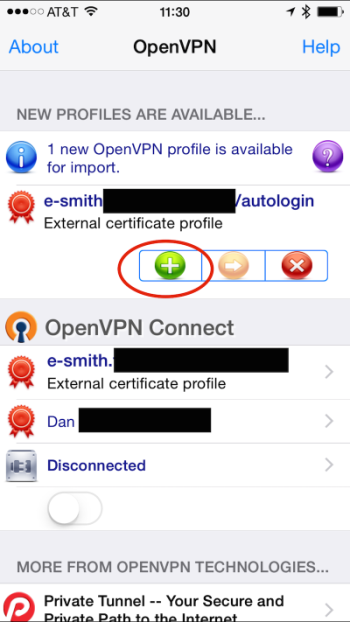
This will take a moment to sync. Once that is completed, open the OpenVPN Connect app on your device. It will inform you that there's a new profile available for import. On that screen, tap the green + button.
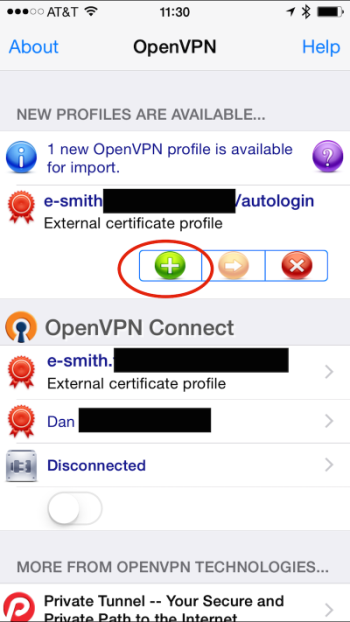
The app will open the profile and indicate that it isn't associated with an identity by showing "None selected". Tap where it says "None selected" to choose an identity profile.
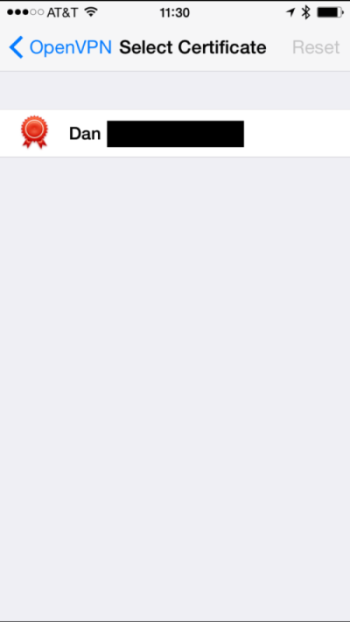
Next, the app will list your available identity profiles. Choose the one you want to associate with this OpenVPN connection.
Configuration is now complete. You can connect to your OpenVPN server using the slider on the screen.
Default key properties
these properties can be modified simply by issuing
config setprop openvpn-routed property newvalue
to reset to default, simply issue:
config delprop openvpn-routed property
where you have to replace property and newvalue with what you want.
| db | Key | Type | Property | Default | Allowed | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| configuration | openvpn-routed | service | ||||
| Protocol | udp | udp / tcp | ||||
| UDPPort | 1194 | |||||
| TCPPort | 1194 | |||||
| Authentication | CrtWithPass | |||||
| Network | 192.168.29.0/255.255.255.0 | user defined | ||||
| PushLocalNetworks | enabled | enabled / disabled | ||||
| RedirectGateway | disabled | enabled / disabled | ||||
| Mtu | none | [nnnn] | ||||
| Fragment | none | |||||
| DuplicateCN | disabled | enabled / disabled | ||||
| PassTOS | enabled | enabled / disabled | ||||
| Compression | enabled | enabled / disabled | ||||
| MaxClients | none | 1 - 254 | ||||
| ConfigRequired | disabled | enabled / disabled | ||||
| Verbose | 3 | [n] | ||||
| Cipher | None | Various. AES-128-CBC | Default BF-CBC deprecated | |||
| HMAC | None | Various. SHA256 | Default SHA1 deprecated | |||
| CrlUrl | None | http://url/phpki/index.php?stage=dl_crl_pem |
you can also set the property PushRoute to disabled to any network in networks db to avoid the contrib to push the network to the client
Workarounds and known issues
if you migrate from SME8 to SME9 and are not able to connect after correctly migrating your certificates, this might be related to not secure enough algorithm. CentOS 6.9 release notes state that "Support for insecure cryptographic protocols and algorithms has been dropped. This affects usage of MD5, SHA0, RC4 and DH parameters shorter than 1024 bits." Of course real solution would be to migrate all your certs to better algorithm.
workaround :
echo -e "LegacySigningMDs md2 md5\nMinimumDHBits 512\n" >> /etc/pki/tls/legacy-settings
service openvpn-routed restart
Bugs
Please raise bugs under the SME-Contribs section in bugzilla and select the smeserver-openvpn-routed component or use this link
| ID | Product | Version | Status | Summary (2 tasks) ⇒ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12379 | SME Contribs | 10.0 | CONFIRMED | remove /var/service/openvpn-routed |
| 12258 | SME Contribs | 10.0 | CONFIRMED | chown error |
Changelog
Only versions released in smecontrib are listed here.
2022/11/23 Jean-Philippe Pialasse 0.1.6-7.sme
- log to a dedicated file [SME: 12243]
- Re-build and link to latest devtools [SME: 11997]
- add to core backup [SME: 11997]
2021/04/01 Jean-Philippe Pialasse 0.1.6-4.sme
- autoconfiguration if openvpn-bridge is isntalled and configured [SME: 11336]
- reworked systemd unit and scripts
- new property HMAC forced to SHA256, instead of insecure default SHA1 [SME: 9925]
- Cipher now enforced to AES-128-CBC, instead of insecure default Blowfish [SME: 9919]
2021/02/04 Brian Read 0.1.6-2.sme
- Initial import to SME10 [SME: 11336]
Other articles in this category
Ipsec, Libreswan, Libreswan-xl2tpd, OpenVPN, OpenVPN Bridge, OpenVPN Bridge/fr, OpenVPN Routed, OpenVPN SiteToSite, SME Server wishlist, SoftEther VPN, Softethervpn-server, VPN, Wireguard, Wireguard/fr
