Difference between revisions of "SME Server:Documentation:Administration Manual:Chapter2"
m (Replaced Template:drawBox* (deprecated) with Template:* box) |
m (Surrounded language template with noinclude tags) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{Languages}} | + | <noinclude>{{Languages}}</noinclude> |
===The role of the SME Server=== | ===The role of the SME Server=== | ||
Your SME Server manages your connection to the Internet by routing Internet data packets to and from your network (which allows all the computers on your network to share a single Internet connection) and by providing security for your network, minimizing the risk of intrusions. When one of your local computers contacts the Internet, or is contacted by an outside machine on the Internet, the SME Server not only routes that connection, but seamlessly interposes itself into the communication. This prevents a direct connection from being established between an external computer on the Internet and a computer on your local network thereby significantly reducing the risk of intrusion onto your network. | Your SME Server manages your connection to the Internet by routing Internet data packets to and from your network (which allows all the computers on your network to share a single Internet connection) and by providing security for your network, minimizing the risk of intrusions. When one of your local computers contacts the Internet, or is contacted by an outside machine on the Internet, the SME Server not only routes that connection, but seamlessly interposes itself into the communication. This prevents a direct connection from being established between an external computer on the Internet and a computer on your local network thereby significantly reducing the risk of intrusion onto your network. | ||
Revision as of 12:39, 9 May 2008
The role of the SME Server
Your SME Server manages your connection to the Internet by routing Internet data packets to and from your network (which allows all the computers on your network to share a single Internet connection) and by providing security for your network, minimizing the risk of intrusions. When one of your local computers contacts the Internet, or is contacted by an outside machine on the Internet, the SME Server not only routes that connection, but seamlessly interposes itself into the communication. This prevents a direct connection from being established between an external computer on the Internet and a computer on your local network thereby significantly reducing the risk of intrusion onto your network.
Your server also provides services - including e-mail, web access and a powerful file sharing and collaboration feature called "i-bays" - that allow you to communicate better internally and with the rest of the world using the Internet. Throughout this user's guide, the word gateway is used to mean the computer that acts as the interface between your local, internal network and the external world.
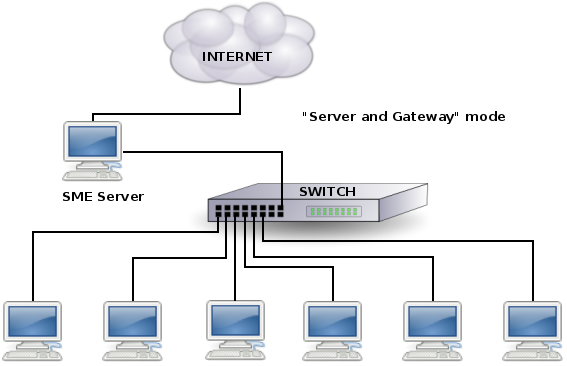 >>++Server and Gateway Mode++]]
If you prefer, you can also run your SME Server in "server-only" mode. In "server-only" mode, your server provides your network with services, but not the routing and security functions associated with the role of "gateway". The server-only mode is typically used for networks already behind a firewall. In that configuration, the firewall fulfills the role of gateway, providing routing and network security.
>>++Server and Gateway Mode++]]
If you prefer, you can also run your SME Server in "server-only" mode. In "server-only" mode, your server provides your network with services, but not the routing and security functions associated with the role of "gateway". The server-only mode is typically used for networks already behind a firewall. In that configuration, the firewall fulfills the role of gateway, providing routing and network security.
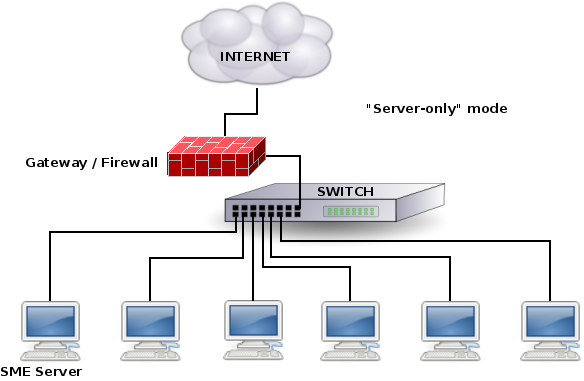 >>++Server only Mode++]]
Once installed, your SME Server can be configured and managed remotely. Routine administration is handled from your desktop using a web-based interface, so only on rare occasions will you require direct access to the server computer. Once installation is complete, most customers put the server in an out-of-the-way place like a utility closet. If you wish, you can disconnect the keyboard and monitor. (Note that some computers may not operate correctly without an attached keyboard.)
>>++Server only Mode++]]
Once installed, your SME Server can be configured and managed remotely. Routine administration is handled from your desktop using a web-based interface, so only on rare occasions will you require direct access to the server computer. Once installation is complete, most customers put the server in an out-of-the-way place like a utility closet. If you wish, you can disconnect the keyboard and monitor. (Note that some computers may not operate correctly without an attached keyboard.)