Difference between revisions of "Backup of ESXi Virtual Machines using Affa"
(revert to use Dropbear 0.49 from ESXi Distro) |
m |
||
| Line 99: | Line 99: | ||
Verify the download | Verify the download | ||
wget http://mirror.contribs.org/smeserver/contribs/michaelw/sme7/Affa2/affa-esxi-setup-02.tgz.md5sum | wget http://mirror.contribs.org/smeserver/contribs/michaelw/sme7/Affa2/affa-esxi-setup-02.tgz.md5sum | ||
| − | md5sum -c affa-esxi-setup- | + | md5sum -c affa-esxi-setup-02.tgz.md5sum |
Unpack it | Unpack it | ||
tar xzf affa-esxi-setup-02.tgz | tar xzf affa-esxi-setup-02.tgz | ||
Revision as of 22:03, 11 November 2008
Introduction
As of version 2, Affa supports hot backing up virtual machines running on the VMWare ESXi server. It uses the VMware Infrastructure Perl Toolkit to communicate with the EXSi and rsync over ssh to transfer the data. Before the backup starts, the state of the running VM is freezed by creating a snapshot of all its disks. After the freezed virtual disk files were backed up, the snapshot is deleted and the config points to the just backed up disks again. Then, as a last step the config files are backed up.
A restore of a VM can be done by simply copying back all archived files to the original location on the ESXi host. It is also possible to copy the files to a different directory (or to another ESXi server) and add the vmx file to the inventory.
Preparing the Affa Server
Install the VMware Infrastructure (VI) Perl Toolkit
Download the VI Perl Toolkit tarball from the VMWare web site: http://www.vmware.com/support/developer/viperltoolkit/
Login as root and run:
/usr/bin/yum install openssl-devel /usr/bin/yum --enable=dag install perl-XML-SAX tar xzf VMware-VIPerl-1.6.0-104313.i386.tar.gz cd vmware-viperl-distrib ./vmware-install.pl
Ignore this warning: The following Perl modules were found on the system but may be too old to work with VIPerl: URI XML::NamespaceSupport
Install Affa Version 2 beta
Install the latest Affa 2.x beta version. Download the RPM from http://mirror.contribs.org/smeserver/contribs/michaelw/sme7/Affa2
/usr/bin/yum --enable=smecontribs localinstall smeserver-affa-2.0.0-beta*.noarch.rpm
Preparing the ESXi Host for use with Affa
To make the ESXi server ready to cooperate with Affa you must install the rsync program, enable the ssh service, configure passwordless ssh login and add a user for communication using the VMware Infrastructure (VI) Perl Toolkit.
Adding an ESXi User with restricted Permissions
Run the Virtual Infrastructure Client and logon to the ESXi host.
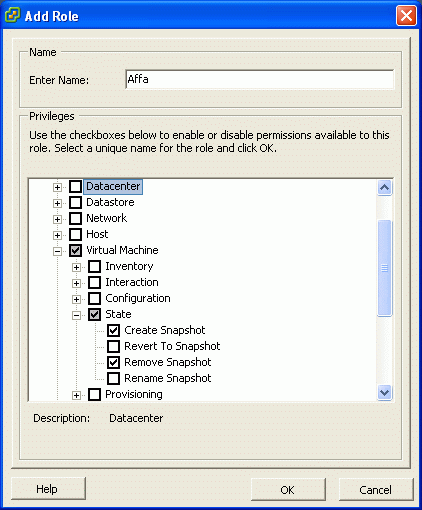
Adding Affa role
Switch to the Administration module and add a new role with permissions to create and delete snapshots
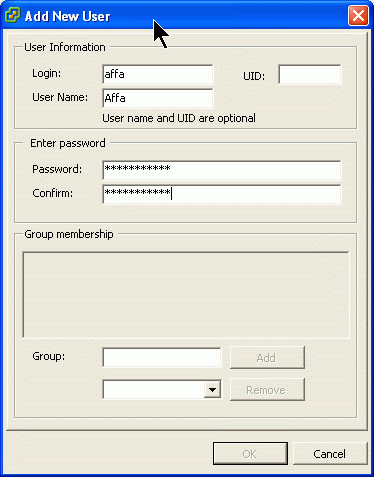
Adding Affa user
Switch back to the Inventory module and add a new user with password:
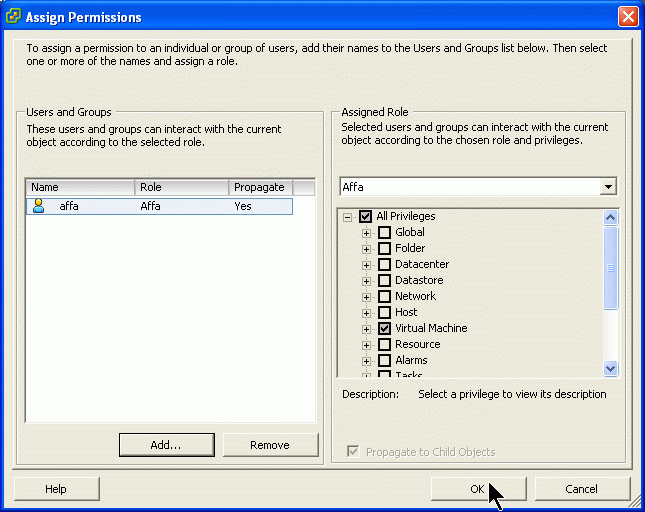
Assigning permissions
In the Permission Tab assign the new role to the new user.
Configuring SSH and RSYNC on the ESX3i Host
On ESXi the SSH service Dropbear is installed but disabled. To use rsync the SSH service must be enabled and the rsync program must be installed. To enable passwordless login a .ssh directory for storing the keys must be created.
A script is provided that does this: To set up ESXi for use with Affa we must:
- enable SSH service by configuring inetd.conf and restarting the inetd service
- install rsync (statically linked binary)
- create a /root home directory with a .ssh sub directory to store the public keys for password-less login
- link the .ssh directory to the non-volatile USB device
- add a command to /etc/rc.local that executes all the steps above at boot time
# enable ssh service sed -ie 's/^#\(ssh.*\)/\1/' /etc/inetd.conf # reload inetd configuration kill -HUP `ps | grep inetd | sed -e 's/ .*//'` # install rsync 3.0.4 statically linked cp -a /bootbank/bexi/rsync-static /bin/rsync # root home dir for storing public keys mkdir -p /bootbank/bexi/root/.ssh touch /bootbank/bexi/root/.ssh/authorized_keys touch /bootbank/bexi/root/.ssh/known_hosts # link .ssh dir to non-volatile USB location mkdir -p /root ln -fs /bootbank/bexi/root/.ssh /root/ # set new home dir for user root sed -ie 's#^\(root:.*\)\(:/:\)\(.*\)#\1:/root:\3#' /etc/passwd # add execution of this script to rc.local grep -v "#BEXI$" < /etc/rc.local > /etc/rc.local.affa; mv -f /etc/rc.local.affa /etc/rc.local echo "test -f /bootbank/bexi/affa-setup.sh && /bootbank/bexi/affa-setup.sh #BEXI" >> /etc/rc.local echo "test ! -d /root && sed -ie 's#^\(root:.*\)\(:/root:\)\(.*\)#\1:/:\3#' /etc/passwd #BEXI" >> /etc/rc.local
Download and install the skript
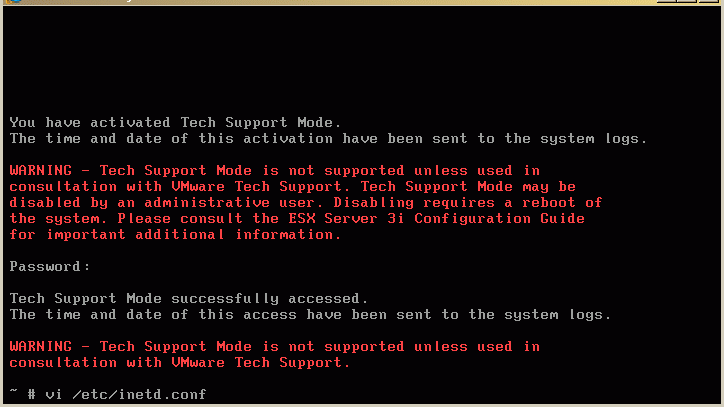
On the ESXi Server console hit Alt-F1 to get the service shell. Now blind-type the word unsupported to unlock the shell.
Login with the root password.
Download the tarball. The tarball contains all binaries and the script.
cd /bootbank wget http://mirror.contribs.org/smeserver/contribs/michaelw/sme7/Affa2/affa-esxi-setup-02.tgz
Verify the download
wget http://mirror.contribs.org/smeserver/contribs/michaelw/sme7/Affa2/affa-esxi-setup-02.tgz.md5sum md5sum -c affa-esxi-setup-02.tgz.md5sum
Unpack it
tar xzf affa-esxi-setup-02.tgz rm affa-esxi-setup-02.tgz*
and run the script
./bexi/affa-setup.sh
Now you can ssh login and use rsync.
Setting up an Affa job
The following assumes, that you are already familiar with configuring Affa and only focus on the ESXi specific parts.
Assume you want to backup the virtual machine named 'myvm' on ESXi server with IP 10.200.48.5.
1. log into the 'affabox' and copy the config helper script
cp -a /usr/lib/affa/jobconfig-esxi-sample.pl /root/esxi-myvm-job.pl
2. edit /root/esxi-myvm-job.pl and set
my $jobname='esxi-myvm';
and
'remoteHostName‘=>'10.200.48.5',
3. tell Affa that this job backups a ESXi virtual machine
'ESXi' => 'yes',
4. set the VM name
'ESXiVMName' => 'myvm',
5. set the username and password (this is the ESXi User with restricted permissions created above)
'ESXiUsername' => 'affa', 'ESXiPassword' => 'secret',
6. save the script, then run it
/root/esxi-myvm-job.pl
7. send the public key
affa --send-key esxi-myvm
8. run the job manually
affa --run esxi-myvm
When the Affa job starts, you can watch the snapshot create task in the Virtual Infrastructure Client.
The name of the snaphot starts with "BEXI-". Do not delete it or revert to it while Affa is running.
Uninstall
SSH login as root on the ESXi host and run these commands carefully:
grep -v "#BEXI" < /etc/rc.local >/etc/rc.local.affa; mv -f /etc/rc.local.affa /etc/rc.local sed -e 's#^\(root:.*\)\(:/root:\)\(.*\)#\1:/:\3#' < /etc/passwd > /etc/passwd.affa; mv -f /etc/passwd.affa /etc/passwd sed -e 's/^\(ssh.*\)/#\1/' < /etc/inetd.conf > /etc/inetd.conf.affa; mv -f /etc/inetd.conf.affa /etc/inetd.conf kill -HUP `ps | grep inetd | sed -e 's/ .*//'` rm -rf /bin/rsync /root /bootbank/bexi tar -C / -xzf /bootbank/environ.tgz sbin/dropbearmulti
Addtional Information
How to make the statically linked Rsync Binary
1. download the source from http://rsync.samba.org/
2. unpack the tarball
tar xzf rsync-3.0.4.tar.gz cd rsync-3.0.4
3. build the statically linked binary
make CFLAGS="-static" EXEEXT="-static" strip rsync-static