Difference between revisions of "Gitea install"
m |
|||
| (25 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | This is how I installed the latest version of Gitea (https://gitea.io) on my smeserver build box | + | ====Installation==== |
| + | <tabs container=""><tab name="For SME10"> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Gitea is an open-source forge software package for hosting software development version control using Git as well as other collaborative features like bug tracking, wikis, and code review. | ||
| + | |||
| + | This is how I installed the latest version of Gitea (https://gitea.io) on my smeserver build box (this is running smeserver v10.1 in serveronly) | ||
| + | |||
| + | This will work for a Centos 7 build as well. | ||
{{Note box|There is a smeserver contrib for Git and gitweb, but I did not use these as they only provide older versions of git, whereas we wanted the latest versions for use with gitea}} | {{Note box|There is a smeserver contrib for Git and gitweb, but I did not use these as they only provide older versions of git, whereas we wanted the latest versions for use with gitea}} | ||
| − | First we need to install git (latest version at the time)<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | + | First we need to install git (latest stable version at the time)<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> |
export GITVER=2.39.1-1 | export GITVER=2.39.1-1 | ||
wget http://opensource.wandisco.com/centos/7/git/x86_64/git-${GITVER}.WANdisco.x86_64.rpm | wget http://opensource.wandisco.com/centos/7/git/x86_64/git-${GITVER}.WANdisco.x86_64.rpm | ||
| Line 19: | Line 26: | ||
chown root:git /etc/gitea | chown root:git /etc/gitea | ||
chmod 770 /etc/gitea | chmod 770 /etc/gitea | ||
| − | </syntaxhighlight>Now we want to set it up as a service and ensure that it will be restarted on reboot.<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | + | </syntaxhighlight> |
| − | + | Now we want to set it up as a service and ensure that it will be restarted on reboot. | |
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/go-gitea/gitea/main/contrib/systemd/gitea.service -O /usr/lib/systemd/system/gitea.service | wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/go-gitea/gitea/main/contrib/systemd/gitea.service -O /usr/lib/systemd/system/gitea.service | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | The following is ONLY needed on an smeserver build | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
mkdir /usr/lib/systemd/system/gitea.service.d | mkdir /usr/lib/systemd/system/gitea.service.d | ||
cat <<EOT > /usr/lib/systemd/system/gitea.service.d/50koozali.conf | cat <<EOT > /usr/lib/systemd/system/gitea.service.d/50koozali.conf | ||
| Line 27: | Line 38: | ||
WantedBy=sme-server.target | WantedBy=sme-server.target | ||
EOT | EOT | ||
| + | config set gitea service status enabled | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | Now we setup gitea on your server | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| + | systemctl enable --now gitea | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | Access the setup page via a browser http://<your-smeserver-IP>:3000 | ||
| + | |||
| + | I found it easiest to just use SQLite3 (built in to smeserver v10) | ||
| + | |||
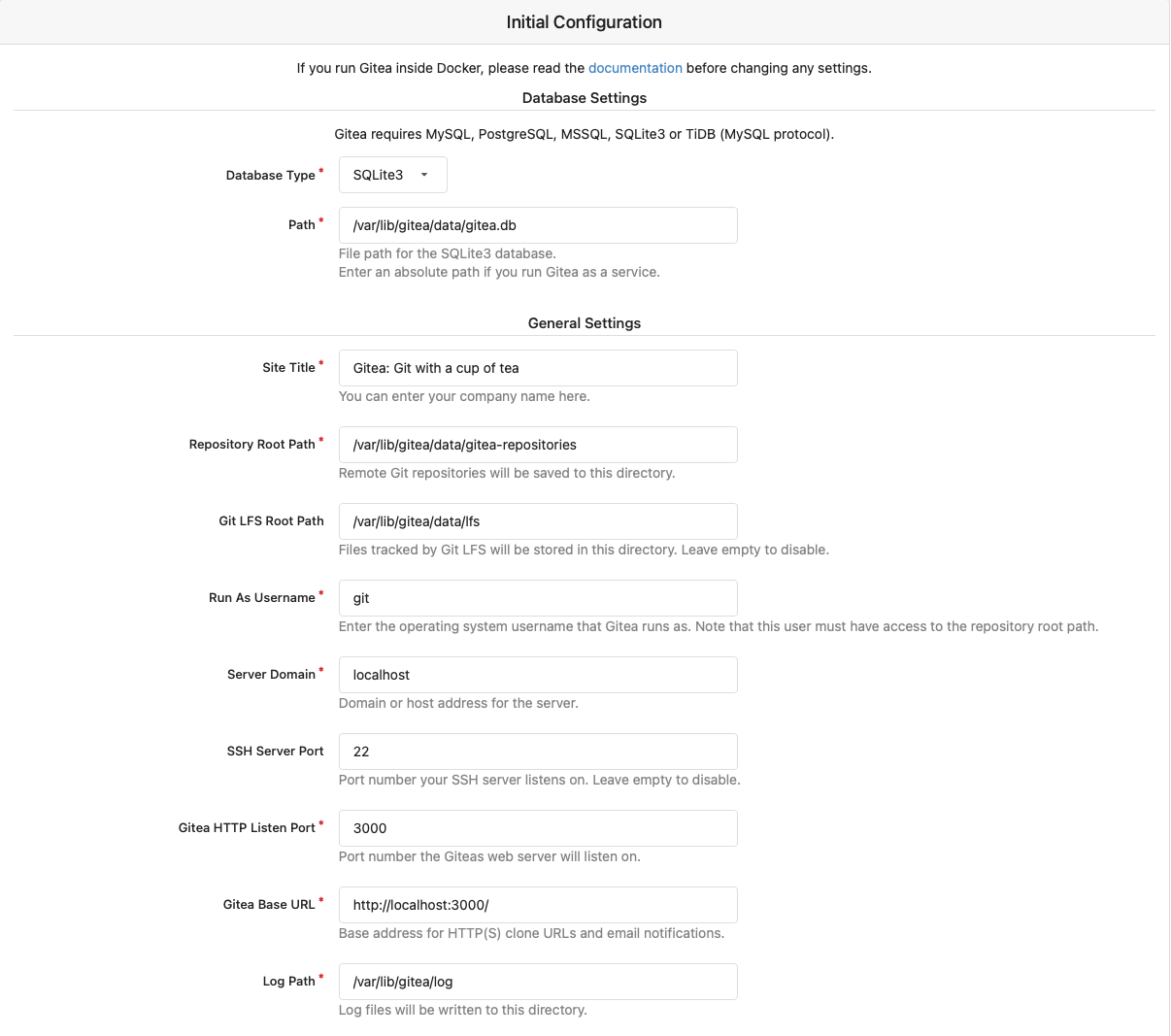
| + | Make sure that you set your Server Domain and Gitea Base URL to the correct values for your server. | ||
| + | [[File:Screenshot 2023-03-19 at 6.12.10 pm.png|frame|alt=|none]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | You will likely have to refresh the browser and then it will ask you to login. | ||
| + | |||
| + | You can setup your users via the web interface. | ||
| + | |||
| + | If you are having problems accessing gitea, check the app.ini file to ensure that the ROOT_URL is correct in<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| + | nano /etc/gitea/app.ini | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight>if you change it, you'll need to restart gitea<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| + | systemctl restart gitea | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | </ | + | </tab> |
| − | + | <tab name="For Rocky 8"> | |
| − | + | Gitea is an open-source forge software package for hosting software development version control using Git as well as other collaborative features like bug tracking, wikis, and code review. | |
| − | I found it easiest to just use SQLite3 ( | + | =====Prerequisites===== |
| + | * Rocky Linux 8 installed | ||
| + | * Full SSH root access. | ||
| + | * Gitea supports the following databases. | ||
| + | * SQLite | ||
| + | * PostgreSQL | ||
| + | * MySQL | ||
| + | * MariaDB | ||
| + | * TiDB | ||
| + | * MSSQL | ||
| + | |||
| + | In the guide below, we’ll use SQLite as the database for Gitea. You can pick any of the supported databases in your installation as needed, just need to create db, user and password and use same details when in setup for the gitea web interface. | ||
| + | |||
| + | This is what I did on a bare Rocky 8 minimal install | ||
| + | |||
| + | First we need to install git and any required pkgs | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| + | dnf install git git-lfs policycoreutils-python-utils wget nano | ||
| + | useradd git | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | Next we'll install gitea ([https://dl.gitea.com/gitea/ latest stable version at the time]) | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| + | export GITEAVER=1.20.5 | ||
| + | wget https://github.com/go-gitea/gitea/releases/download/v${GITEAVER}/gitea-${GITEAVER}-linux-amd64 -O /usr/local/bin/gitea | ||
| + | chmod +x /usr/local/bin/gitea | ||
| + | mkdir -p /etc/gitea /var/lib/gitea/{custom,data,indexers,public,log} | ||
| + | chown git:git /var/lib/gitea/{data,indexers,log} | ||
| + | chmod 750 /var/lib/gitea/{data,indexers,log} | ||
| + | chown root:git /etc/gitea | ||
| + | chmod 770 /etc/gitea | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | Now we want to set it up as a service and set security settings (selinux and firewall). | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| + | wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/go-gitea/gitea/main/contrib/systemd/gitea.service -O /usr/lib/systemd/system/gitea.service | ||
| + | semanage fcontext -a -t public_content_rw_t "/var/lib/gitea/data/gitea-repositories(/.*)?" | ||
| + | restorecon -r -v /var/lib/gitea/data/gitea-repositories | ||
| + | firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-port=3000/tcp | ||
| + | firewall-cmd --reload | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | Now we setup gitea on your server | ||
| + | {{Note box|Gitea will wait for you to run the web setup, but as we are starting this as a service, the service will timeout if you leave it. The service will auto-restart, so you can try to connect and setup again, or you can manually restart the gitea service.}} | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| + | systemctl enable --now gitea | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | Access the setup page via a browser http://<your-smeserver-IP>:3000 | ||
| + | |||
| + | I found it easiest to just use SQLite3 (already installed) | ||
Make sure that you set your Server Domain and Gitea Base URL to the correct values for your server. | Make sure that you set your Server Domain and Gitea Base URL to the correct values for your server. | ||
| Line 41: | Line 120: | ||
You can setup your users via the web interface. | You can setup your users via the web interface. | ||
| − | If you are having problems accessing gitea, check the app.ini file to ensure that | + | If you are having problems accessing gitea, check the app.ini file to ensure that the ROOT_URL is correct in |
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
nano /etc/gitea/app.ini | nano /etc/gitea/app.ini | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | if you change it, you'll need to restart gitea | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| + | systemctl restart gitea | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | </tab> | ||
| + | </tabs> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Using Maria DB >= 10.4=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | From here: | ||
| + | |||
| + | https://docs.gitea.com/installation/database-prep | ||
| + | |||
| + | For local database: | ||
| + | |||
| + | SET old_passwords=0; | ||
| + | CREATE USER 'gitea'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'gitea'; | ||
| + | |||
| + | Create database with UTF-8 charset and collation. Make sure to use utf8mb4 charset instead of utf8 as the former supports all Unicode characters (including emojis) beyond Basic Multilingual Plane. Also, collation chosen depending on your expected content. When in doubt, use either unicode_ci or general_ci. | ||
| + | |||
| + | CREATE DATABASE giteadb CHARACTER SET 'utf8mb4' COLLATE 'utf8mb4_unicode_ci'; | ||
| + | |||
| + | Grant all privileges on the database to database user created above. | ||
| + | |||
| + | For local database: | ||
| + | |||
| + | GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON giteadb.* TO 'gitea'; | ||
| + | FLUSH PRIVILEGES; | ||
| + | |||
| + | Quit from database console using 'exit' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Test your connection | ||
| + | |||
| + | mysql -u gitea -p giteadb | ||
| + | |||
| + | Now you can use the Database Type "Maria DB" in your setup. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===LDAP settings=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | https://docs.gitea.com/features/authentication | ||
| + | |||
| + | Under SME v10 we can authenticate users against the local LDAP server. | ||
| + | |||
| + | On my server I had already set up a LDAP authentication user called 'auth' rather than using the admin account. | ||
| + | I also set up a group called 'it_dept' for restricting user access. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Site Administration, Authentication Sources | ||
| + | |||
| + | Add Authentication Source | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Settings==== | ||
| + | Authentication Name : Choose a name | ||
| + | Security Protocol: StartTLS | ||
| + | Host: Your LDAP host | ||
| + | Port: 389 | ||
| + | Bind DN: uid=auth,ou=Users,dc=yourdomain,dc=com | ||
| + | Bind Password: "password of 'auth' user" | ||
| + | User Search Base: ou=Users,dc=yourdomain,dc=com | ||
| + | User Filter: (&(objectClass=posixAccount)(|(uid=%[1]s)(mail=%[1]s))) | ||
| + | |||
| + | First Name Attribute: givenName | ||
| + | Surname Attribute: sn | ||
| + | Email Attribute: mail | ||
| + | |||
| + | Enable LDAP Groups | ||
| + | |||
| + | Group Search Base DN: ou=Groups,dc=yourdomain,dc=com | ||
| + | Group Attribute Containing List Of Users :memberUID | ||
| + | Verify group membership in LDAP: (cn=it_dept) | ||
| + | |||
| + | Fetch Attributes in Bind DN Context: enabled | ||
| + | This Authentication source is Activated: enabled | ||
| + | |||
| + | Enable user synchronization: enabled (after you have checked your settings!) | ||
| + | |||
| + | This option enables a periodic task that synchronizes the Gitea users with the LDAP server. The default period is every 24 hours but that can be changed in the app.ini file. See the cron.sync_external_users section in the sample app.ini for detailed comments about that section. The User Search Base and User Filter settings described above will limit which users can use Gitea and which users will be synchronized. When initially run the task will create all LDAP users that match the given settings so take care if working with large Enterprise LDAP directories. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Notes==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Once this is enabled a user logging in will have a gitea account created and synced. | ||
| + | |||
| + | You can also change the accounts between Local and LDAP | ||
| + | |||
| + | Identity & Access, User Accounts | ||
| + | |||
| + | Authentication Source: LDAP | ||
| + | Authentication Sign-In Name: Match the LDAP name | ||
| + | |||
| + | Update and test login. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Developer]] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:07, 25 February 2024
Installation
Gitea is an open-source forge software package for hosting software development version control using Git as well as other collaborative features like bug tracking, wikis, and code review.
This is how I installed the latest version of Gitea (https://gitea.io) on my smeserver build box (this is running smeserver v10.1 in serveronly)
This will work for a Centos 7 build as well.
First we need to install git (latest stable version at the time)
export GITVER=2.39.1-1
wget http://opensource.wandisco.com/centos/7/git/x86_64/git-${GITVER}.WANdisco.x86_64.rpm
wget http://opensource.wandisco.com/centos/7/git/x86_64/perl-Git-${GITVER}.WANdisco.noarch.rpm
yum localinstall git-${GITVER}.WANdisco.x86_64.rpm perl-Git-${GITVER}.WANdisco.noarch.rpm
export GITEAVER=1.18.5
wget https://github.com/go-gitea/gitea/releases/download/v${GITEAVER}/gitea-${GITEAVER}-linux-amd64 -O /usr/local/bin/gitea
chmod +x /usr/local/bin/gitea
useradd git
mkdir -p /etc/gitea /var/lib/gitea/{custom,data,indexers,public,log}
chown git:git /var/lib/gitea/{data,indexers,log}
chmod 750 /var/lib/gitea/{data,indexers,log}
chown root:git /etc/gitea
chmod 770 /etc/gitea
Now we want to set it up as a service and ensure that it will be restarted on reboot.
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/go-gitea/gitea/main/contrib/systemd/gitea.service -O /usr/lib/systemd/system/gitea.service
The following is ONLY needed on an smeserver build
mkdir /usr/lib/systemd/system/gitea.service.d
cat <<EOT > /usr/lib/systemd/system/gitea.service.d/50koozali.conf
[Install]
WantedBy=sme-server.target
EOT
config set gitea service status enabled
Now we setup gitea on your server
systemctl enable --now gitea
Access the setup page via a browser http://<your-smeserver-IP>:3000
I found it easiest to just use SQLite3 (built in to smeserver v10)
Make sure that you set your Server Domain and Gitea Base URL to the correct values for your server.
You will likely have to refresh the browser and then it will ask you to login.
You can setup your users via the web interface.
If you are having problems accessing gitea, check the app.ini file to ensure that the ROOT_URL is correct innano /etc/gitea/app.ini
systemctl restart gitea
Gitea is an open-source forge software package for hosting software development version control using Git as well as other collaborative features like bug tracking, wikis, and code review.
Prerequisites
- Rocky Linux 8 installed
- Full SSH root access.
- Gitea supports the following databases.
* SQLite * PostgreSQL * MySQL * MariaDB * TiDB * MSSQL
In the guide below, we’ll use SQLite as the database for Gitea. You can pick any of the supported databases in your installation as needed, just need to create db, user and password and use same details when in setup for the gitea web interface.
This is what I did on a bare Rocky 8 minimal install
First we need to install git and any required pkgs
dnf install git git-lfs policycoreutils-python-utils wget nano
useradd git
Next we'll install gitea (latest stable version at the time)
export GITEAVER=1.20.5
wget https://github.com/go-gitea/gitea/releases/download/v${GITEAVER}/gitea-${GITEAVER}-linux-amd64 -O /usr/local/bin/gitea
chmod +x /usr/local/bin/gitea
mkdir -p /etc/gitea /var/lib/gitea/{custom,data,indexers,public,log}
chown git:git /var/lib/gitea/{data,indexers,log}
chmod 750 /var/lib/gitea/{data,indexers,log}
chown root:git /etc/gitea
chmod 770 /etc/gitea
Now we want to set it up as a service and set security settings (selinux and firewall).
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/go-gitea/gitea/main/contrib/systemd/gitea.service -O /usr/lib/systemd/system/gitea.service
semanage fcontext -a -t public_content_rw_t "/var/lib/gitea/data/gitea-repositories(/.*)?"
restorecon -r -v /var/lib/gitea/data/gitea-repositories
firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-port=3000/tcp
firewall-cmd --reload
Now we setup gitea on your server
systemctl enable --now gitea
Access the setup page via a browser http://<your-smeserver-IP>:3000
I found it easiest to just use SQLite3 (already installed)
Make sure that you set your Server Domain and Gitea Base URL to the correct values for your server.
You will likely have to refresh the browser and then it will ask you to login.
You can setup your users via the web interface.
If you are having problems accessing gitea, check the app.ini file to ensure that the ROOT_URL is correct in
nano /etc/gitea/app.ini
if you change it, you'll need to restart gitea
systemctl restart gitea
Using Maria DB >= 10.4
From here:
https://docs.gitea.com/installation/database-prep
For local database:
SET old_passwords=0; CREATE USER 'gitea'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'gitea';
Create database with UTF-8 charset and collation. Make sure to use utf8mb4 charset instead of utf8 as the former supports all Unicode characters (including emojis) beyond Basic Multilingual Plane. Also, collation chosen depending on your expected content. When in doubt, use either unicode_ci or general_ci.
CREATE DATABASE giteadb CHARACTER SET 'utf8mb4' COLLATE 'utf8mb4_unicode_ci';
Grant all privileges on the database to database user created above.
For local database:
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON giteadb.* TO 'gitea'; FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
Quit from database console using 'exit'
Test your connection
mysql -u gitea -p giteadb
Now you can use the Database Type "Maria DB" in your setup.
LDAP settings
https://docs.gitea.com/features/authentication
Under SME v10 we can authenticate users against the local LDAP server.
On my server I had already set up a LDAP authentication user called 'auth' rather than using the admin account. I also set up a group called 'it_dept' for restricting user access.
Site Administration, Authentication Sources
Add Authentication Source
Settings
Authentication Name : Choose a name Security Protocol: StartTLS Host: Your LDAP host Port: 389 Bind DN: uid=auth,ou=Users,dc=yourdomain,dc=com Bind Password: "password of 'auth' user" User Search Base: ou=Users,dc=yourdomain,dc=com User Filter: (&(objectClass=posixAccount)(|(uid=%[1]s)(mail=%[1]s)))
First Name Attribute: givenName Surname Attribute: sn Email Attribute: mail
Enable LDAP Groups
Group Search Base DN: ou=Groups,dc=yourdomain,dc=com Group Attribute Containing List Of Users :memberUID Verify group membership in LDAP: (cn=it_dept)
Fetch Attributes in Bind DN Context: enabled This Authentication source is Activated: enabled
Enable user synchronization: enabled (after you have checked your settings!)
This option enables a periodic task that synchronizes the Gitea users with the LDAP server. The default period is every 24 hours but that can be changed in the app.ini file. See the cron.sync_external_users section in the sample app.ini for detailed comments about that section. The User Search Base and User Filter settings described above will limit which users can use Gitea and which users will be synchronized. When initially run the task will create all LDAP users that match the given settings so take care if working with large Enterprise LDAP directories.
Notes
Once this is enabled a user logging in will have a gitea account created and synced.
You can also change the accounts between Local and LDAP
Identity & Access, User Accounts
Authentication Source: LDAP Authentication Sign-In Name: Match the LDAP name
Update and test login.