Difference between revisions of "SME Server:Documentation:User Manual:Chapter2"
Unnilennium (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (12 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
===Configuring an email client=== | ===Configuring an email client=== | ||
| − | Your email client application (Outlook, Thunderbird | + | {{note box|You can simplify this process by using the following contrib which helps client auto configuring email access simply giving the email and password [[Autodiscover]]}} |
| + | |||
| + | {{WIP box}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | Your email client application (e.g.: Outlook, Thunderbird, Evolution) requires setting up with information about your email accounts: how to route outgoing email and credentials required to pick up your incoming email. This information is usually entered in the "preferences" or "options" section of the email client. | ||
Most email clients require you to enter the following information: | Most email clients require you to enter the following information: | ||
| Line 15: | Line 19: | ||
The mail client may offer you the choice between POP3 and IMAP operation modes. | The mail client may offer you the choice between POP3 and IMAP operation modes. | ||
| − | '''If you | + | {{warning box|In general we strongly recommend that you use IMAPs which is a much more modern protocol, but POP is supported if you have no other choice}} |
| + | |||
| + | ==== IMAP versus POP3 email ==== | ||
| + | There are two common standards for email management, IMAP and POP3. Your server supports both protocols. You will need to select the protocol that is right for your organization, although IMAP is favoured for almost all situations. | ||
| + | |||
| + | IMAP email, is designed to permit interactive access to multiple mailboxes from multiple client machines. You manage your email on the mail server over the network. You read your email over the network from your desktop, but the email is not stored on your desktop machine - rather, it is permanently stored and managed on the server. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Benefits of IMAP:''' You can access all of your new and stored email from any machine connected to a network. Because all employee email is stored on the server, backup of email is easily accomplished. | ||
| + | |||
| + | IMAP allows better overall management of email across a number of end user devices. Whatever you do on one, is reflected to all others, even adding new folders and moving messages to archive folders. eg you can send on a workstation and see all your sent messages on the phone and so on. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Whatever email you send or receive, folder changes etc at any email client including workstations, phones, remote workstations and even webmail (accessed via web browser from home or anywhere), will all show the same. You can set the email clients to retain local copies of messages if that is important. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Drawbacks of IMAP:''' If you are not connected to a network, new and remote stored email messages are not available to you.(stored emails can be solved with current email clients for desktop - i.e. Thunderbird option to cache the mails for offline working - some clients for mobile devices do this also, practically you'll have the last snapshot from the moment when you were online ) | ||
| + | |||
| + | POP3 is an earlier and ageing email legacy protocol. POP3 was designed to permit on-demand retrieval to a single client machine. Email is stored on the mail server until you retrieve it, at which time it is transferred over the network to your desktop machine and stored in your email box there. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Benefits of POP3:''' Even when you are not connected to your network, you have access to the email stored on your desktop. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Drawbacks of POP3:''' POP3 was not originally intended to support users accessing and managing their email from remote systems. Because your email is stored on your desktop, setting up remote access of your email when you are at a different computer can be complex. | ||
| − | + | ==== Incoming POP3 email service ==== | |
| + | Enable POP3 protocol: Typically, to enable the POP3 protocol for incoming email, you click on a POP3 checkbox or select POP3 from a pull-down menu in the section of your email application dedicated to the incoming mail server. | ||
* Disable IMAP protocol: To disable the IMAP protocol for outgoing mail (not all email client applications have IMAP protocol) click the IMAP checkbox "off". | * Disable IMAP protocol: To disable the IMAP protocol for outgoing mail (not all email client applications have IMAP protocol) click the IMAP checkbox "off". | ||
* Delete read email from server: We recommend you configure your pop3 email client application to delete each message from the server when it has been downloaded to your client application. To do this, click off the checkbox marked "leave mail on server" or click on the checkbox marked "delete mail from server". | * Delete read email from server: We recommend you configure your pop3 email client application to delete each message from the server when it has been downloaded to your client application. To do this, click off the checkbox marked "leave mail on server" or click on the checkbox marked "delete mail from server". | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |+Setting your POP3 account for username@domain.tld | ||
| + | ! | ||
| + | !pop3s | ||
| + | !pop3 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |server name | ||
| + | | colspan="2" |domain.tld | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Port | ||
| + | |995 | ||
| + | |110 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |User Name | ||
| + | | colspan="2" |username | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |connectivity security | ||
| + | |SSL/TLS | ||
| + | |startTLS | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Authentication method | ||
| + | | colspan="2" |normal password | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | + | ==== Incoming IMAP email service ==== | |
| − | |||
* Enable IMAP protocol: Typically, to enable the IMAP protocol for incoming email (note that not all email client applications offer IMAP support) you click on the IMAP checkbox or select IMAP from a pull-down menu in the section of your email client application dedicated to the incoming mail server. | * Enable IMAP protocol: Typically, to enable the IMAP protocol for incoming email (note that not all email client applications offer IMAP support) you click on the IMAP checkbox or select IMAP from a pull-down menu in the section of your email client application dedicated to the incoming mail server. | ||
* Disable POP3 protocol: To disable the POP3 protocol for outgoing mail, click the POP3 checkbox "off". | * Disable POP3 protocol: To disable the POP3 protocol for outgoing mail, click the POP3 checkbox "off". | ||
| Line 31: | Line 77: | ||
First you choose Preferences from the Edit menu and click on Mail Servers as shown in: | First you choose Preferences from the Edit menu and click on Mail Servers as shown in: | ||
| − | [[Image:ScreenshotAccountSettings.jpg ]] | + | [[Image:ScreenshotAccountSettings.jpg |581x581px]] |
| Line 37: | Line 83: | ||
Thunderbird should now be ready to send and receive email. | Thunderbird should now be ready to send and receive email. | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |+Setting your IMAP account for username@domain.tld | ||
| + | ! | ||
| + | !imaps | ||
| + | !imap | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |server name | ||
| + | | colspan="2" |domain.tld | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Port | ||
| + | |993 | ||
| + | |143 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |User Name | ||
| + | | colspan="2" |username | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |connectivity security | ||
| + | |SSL/TLS | ||
| + | |startTLS | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Authentication method | ||
| + | | colspan="2" |normal password | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | ==== | + | ====Outgoing SMTP Email Service==== |
| − | There are | + | There are 3 usual port for submitting an outgoing email. SME Server offers two of them. |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | You can submit on port 25, which is also the regular SMTP port for email exchange between SMTP servers. This method will Require startTLS method after the initial clear connection in order to encrypt the login process and protect your password. SME Server allows you to use this method. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | The legacy 465 port offer implicit SSL encryption upon connection and is the default we suggest with SME. It is not considered a RFC compliant port, but is still used for historical reason in many places. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | The official submission port is 587, offers usually startTLS after initial clear connection, but does not accept any email without an actual login. SME Server does not offers this method. | |
| − | + | {| class="wikitable" | |
| + | |+Setting your SMTP account for username@domain.tld | ||
| + | ! | ||
| + | !smtps | ||
| + | !smtp | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |server name | ||
| + | | colspan="2" |domain.tld | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Port | ||
| + | |465 | ||
| + | |25 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |User Name | ||
| + | | colspan="2" |username | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |connectivity security | ||
| + | |SSL/TLS | ||
| + | |startTLS | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Authentication method | ||
| + | | colspan="2" |normal password | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | + | ====Horde Agenda==== | |
| + | It needs webmail enabled for your server. You can also setup additional agenda from your webmail for every user. | ||
| − | + | # type Caldav | |
| − | + | # address https://domain.tld/horde/rpc.php/principals/username/ | |
| + | # user username | ||
| + | # email username@domain.tld | ||
| + | # use SSL: yes | ||
| − | + | ====Horde Tasks==== | |
| + | It needs webmail enabled for your server. You can also setup additional task lists from your webmail for every user. | ||
| − | + | # type Caldav | |
| + | # address https://domain.tld/horde/rpc.php/principals/username/ | ||
| + | # user username | ||
| + | # email username@domain.tld | ||
| + | # use SSL: yes | ||
| + | ====Horde Address Book==== | ||
| + | It needs webmail enabled for your server. You can also setup additional address books from your webmail for every user. | ||
| − | + | # type Cardav | |
| − | + | # address https://domain.tld/horde/rpc.php/principals/username/ | |
| + | # user username | ||
| + | # email username@domain.tld | ||
| + | # use SSL: yes | ||
| − | === | + | ====LDAP Directory (SME Server internal Address Book)==== |
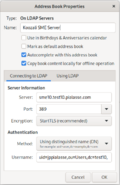
Your SME Server automatically maintains a Directory and populates it with users names and contact details when Admin enters these in the server-manager. Any client program that uses LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol), such as the address book in Thunderbird, will be able to access the Directory - but by default this will be read-only access. For example, with Thunderbird, look under the "Tools" menu and choose "Address Book". Then look under the "File" - "New" menu and select "LDAP Directory". | Your SME Server automatically maintains a Directory and populates it with users names and contact details when Admin enters these in the server-manager. Any client program that uses LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol), such as the address book in Thunderbird, will be able to access the Directory - but by default this will be read-only access. For example, with Thunderbird, look under the "Tools" menu and choose "Address Book". Then look under the "File" - "New" menu and select "LDAP Directory". | ||
| Line 80: | Line 173: | ||
[[Image:Netscape_prefs_directory.png]] | [[Image:Netscape_prefs_directory.png]] | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | The following table is a resume of what you will need to enter depending of your client available settings. There are 3 main configurations : Anonymous, authenticated using starttls and authenticated using the SSL port. Pay attention that some client won't accept to connect if you use a self signed certificate. Also, important to note: | |
| − | * | + | *For the name you wish to give your company directory - any name will do. |
*The LDAP server or Hostname is the name of your web server, in the form www.yourdomain.xxx. | *The LDAP server or Hostname is the name of your web server, in the form www.yourdomain.xxx. | ||
| Line 88: | Line 181: | ||
*The Server Root information can be found on the "Directory" screen in your server-manager (more information on this is available in the next chapter). The usual form, assuming your domain is yourdomain.xxx, is dc=yourdomain,dc=xxx . (No spaces should be entered between the "dc=" statements.) | *The Server Root information can be found on the "Directory" screen in your server-manager (more information on this is available in the next chapter). The usual form, assuming your domain is yourdomain.xxx, is dc=yourdomain,dc=xxx . (No spaces should be entered between the "dc=" statements.) | ||
| − | + | {| class="wikitable" | |
| + | |+LDAP Settings | ||
| + | ! | ||
| + | !clear | ||
| + | !STARTTLS | ||
| + | !SSL | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Name | ||
| + | | colspan="3" |My Koozali SME Server LDAP | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Server | ||
| + | | colspan="3" |domain.tld | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Port | ||
| + | | colspan="2" |389 | ||
| + | |636 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Encryption | ||
| + | |none | ||
| + | |startTLS | ||
| + | |SSL | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Authentication Method | ||
| + | |Anonymous | ||
| + | | colspan="2" |use Distinguished Name (DN) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Username / Bind DN | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | colspan="2" |uid=USERNAME,ou=Users,dc=domain,dc.tld | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Base DN | ||
| + | | colspan="3" |ou=Users,dc=domain,dc.tld | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Snapshot | ||
| + | |[[Image:Netscape_prefs_directory.png|alt=|120x120px]] | ||
| + | |[[Image:Thunderbird_ldap_ssl.png|alt=|120x120px]] | ||
| + | |[[Image:Evolution_LDAP_startls.png|alt=|185x185px]] | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Configuring Your Web Browser=== | ||
| + | Most browsers (Internet Explorer, Firefox etc) are configured using a dialog box called "preferences", "network preferences" or "options". Some browsers need to be configured to access the Internet either directly or via a proxy server. When required, most desktop applications, your web browser included, should be configured as though they were directly accessing the Internet. Although the server uses a security feature known as IP masquerading, thereby creating an indirect connection to the Internet, this is a transparent operation to most of your desktop applications. Hence, you should ensure that the "Direct connection to the Internet" check box is clicked "on" in your web browser. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Under certain circumstances, using a proxy server can improve the perceived performance of your network. The server includes HTTP, FTP and Gopher proxy servers. Normally, we recommend these be disabled in your browser. | ||
| + | |||
| + | If you decided that you do want to use proxy servers [[#3]], you will need to enter the IP address or domain name of the proxy server (i.e. your server) into the configuration screens of your web browser. The port number you will need to enter to connect to the proxy server is 3128. This information is the same for HTTP, Gopher and FTP proxying. | ||
| + | Alternatively your browser can find the proxy details for itself by entering <nowiki>http://proxy/proxy.pac</nowiki> into Automatic proxy configuration URL: | ||
| + | |||
| + | The image below shows how a proxy server would be configured in Mozilla Firefox. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Firefox_connection_settings.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| − | + | ---- | |
| + | [[#3]] Note that laptop users should disable proxy servers when working away from their local area networks. | ||
Latest revision as of 02:09, 15 July 2022
Chapter 2 - Configuring Applications on your Computer
Configuring an email client
Your email client application (e.g.: Outlook, Thunderbird, Evolution) requires setting up with information about your email accounts: how to route outgoing email and credentials required to pick up your incoming email. This information is usually entered in the "preferences" or "options" section of the email client.
Most email clients require you to enter the following information:
User's email address: This is the user account name (as created in the server-manager) followed by @domain name. Typically it will be in the form of username@yourdomain.xxx (e.g. afripp@tofu-dog.com).
Email server (outgoing SMTP mail server): The address of the mail server. As you prefer, you can enter the ip address of the SME Server, or you should be able to use the server's full domain name, like mail.yourdomain.xxx (e.g. mail.tofu-dog.com).
Email account name or username: this is the name before the @ in the email address. For example, the username for "afripp@tofu-dog.com" is " afripp ".
The mail client may offer you the choice between POP3 and IMAP operation modes.
IMAP versus POP3 email
There are two common standards for email management, IMAP and POP3. Your server supports both protocols. You will need to select the protocol that is right for your organization, although IMAP is favoured for almost all situations.
IMAP email, is designed to permit interactive access to multiple mailboxes from multiple client machines. You manage your email on the mail server over the network. You read your email over the network from your desktop, but the email is not stored on your desktop machine - rather, it is permanently stored and managed on the server.
Benefits of IMAP: You can access all of your new and stored email from any machine connected to a network. Because all employee email is stored on the server, backup of email is easily accomplished.
IMAP allows better overall management of email across a number of end user devices. Whatever you do on one, is reflected to all others, even adding new folders and moving messages to archive folders. eg you can send on a workstation and see all your sent messages on the phone and so on.
Whatever email you send or receive, folder changes etc at any email client including workstations, phones, remote workstations and even webmail (accessed via web browser from home or anywhere), will all show the same. You can set the email clients to retain local copies of messages if that is important.
Drawbacks of IMAP: If you are not connected to a network, new and remote stored email messages are not available to you.(stored emails can be solved with current email clients for desktop - i.e. Thunderbird option to cache the mails for offline working - some clients for mobile devices do this also, practically you'll have the last snapshot from the moment when you were online )
POP3 is an earlier and ageing email legacy protocol. POP3 was designed to permit on-demand retrieval to a single client machine. Email is stored on the mail server until you retrieve it, at which time it is transferred over the network to your desktop machine and stored in your email box there.
Benefits of POP3: Even when you are not connected to your network, you have access to the email stored on your desktop.
Drawbacks of POP3: POP3 was not originally intended to support users accessing and managing their email from remote systems. Because your email is stored on your desktop, setting up remote access of your email when you are at a different computer can be complex.
Incoming POP3 email service
Enable POP3 protocol: Typically, to enable the POP3 protocol for incoming email, you click on a POP3 checkbox or select POP3 from a pull-down menu in the section of your email application dedicated to the incoming mail server.
- Disable IMAP protocol: To disable the IMAP protocol for outgoing mail (not all email client applications have IMAP protocol) click the IMAP checkbox "off".
- Delete read email from server: We recommend you configure your pop3 email client application to delete each message from the server when it has been downloaded to your client application. To do this, click off the checkbox marked "leave mail on server" or click on the checkbox marked "delete mail from server".
| pop3s | pop3 | |
|---|---|---|
| server name | domain.tld | |
| Port | 995 | 110 |
| User Name | username | |
| connectivity security | SSL/TLS | startTLS |
| Authentication method | normal password | |
Incoming IMAP email service
- Enable IMAP protocol: Typically, to enable the IMAP protocol for incoming email (note that not all email client applications offer IMAP support) you click on the IMAP checkbox or select IMAP from a pull-down menu in the section of your email client application dedicated to the incoming mail server.
- Disable POP3 protocol: To disable the POP3 protocol for outgoing mail, click the POP3 checkbox "off".
The images below show you the setup sequence in the Mozilla Thunderbird mail client.
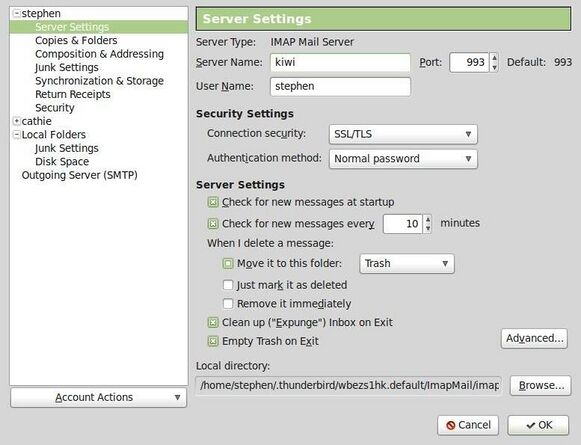
First you choose Preferences from the Edit menu and click on Mail Servers as shown in:
If you have not entered details about your mail server yet, you will need to press the Add button and enter some information. Otherwise, you will select the default mail server listed and click on the the Edit button. This will bring up a screen where you enter the username and choose whether you are using IMAP or POP3:
Thunderbird should now be ready to send and receive email.
| imaps | imap | |
|---|---|---|
| server name | domain.tld | |
| Port | 993 | 143 |
| User Name | username | |
| connectivity security | SSL/TLS | startTLS |
| Authentication method | normal password | |
Outgoing SMTP Email Service
There are 3 usual port for submitting an outgoing email. SME Server offers two of them.
You can submit on port 25, which is also the regular SMTP port for email exchange between SMTP servers. This method will Require startTLS method after the initial clear connection in order to encrypt the login process and protect your password. SME Server allows you to use this method.
The legacy 465 port offer implicit SSL encryption upon connection and is the default we suggest with SME. It is not considered a RFC compliant port, but is still used for historical reason in many places.
The official submission port is 587, offers usually startTLS after initial clear connection, but does not accept any email without an actual login. SME Server does not offers this method.
| smtps | smtp | |
|---|---|---|
| server name | domain.tld | |
| Port | 465 | 25 |
| User Name | username | |
| connectivity security | SSL/TLS | startTLS |
| Authentication method | normal password | |
Horde Agenda
It needs webmail enabled for your server. You can also setup additional agenda from your webmail for every user.
- type Caldav
- address https://domain.tld/horde/rpc.php/principals/username/
- user username
- email username@domain.tld
- use SSL: yes
Horde Tasks
It needs webmail enabled for your server. You can also setup additional task lists from your webmail for every user.
- type Caldav
- address https://domain.tld/horde/rpc.php/principals/username/
- user username
- email username@domain.tld
- use SSL: yes
Horde Address Book
It needs webmail enabled for your server. You can also setup additional address books from your webmail for every user.
- type Cardav
- address https://domain.tld/horde/rpc.php/principals/username/
- user username
- email username@domain.tld
- use SSL: yes
LDAP Directory (SME Server internal Address Book)
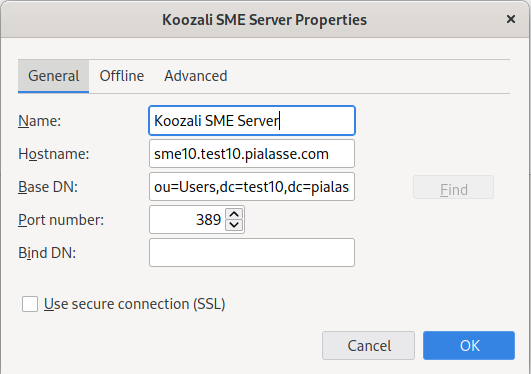
Your SME Server automatically maintains a Directory and populates it with users names and contact details when Admin enters these in the server-manager. Any client program that uses LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol), such as the address book in Thunderbird, will be able to access the Directory - but by default this will be read-only access. For example, with Thunderbird, look under the "Tools" menu and choose "Address Book". Then look under the "File" - "New" menu and select "LDAP Directory".
You will see a dialog box similar to the one shown here.
The following table is a resume of what you will need to enter depending of your client available settings. There are 3 main configurations : Anonymous, authenticated using starttls and authenticated using the SSL port. Pay attention that some client won't accept to connect if you use a self signed certificate. Also, important to note:
- For the name you wish to give your company directory - any name will do.
- The LDAP server or Hostname is the name of your web server, in the form www.yourdomain.xxx.
- The Server Root information can be found on the "Directory" screen in your server-manager (more information on this is available in the next chapter). The usual form, assuming your domain is yourdomain.xxx, is dc=yourdomain,dc=xxx . (No spaces should be entered between the "dc=" statements.)
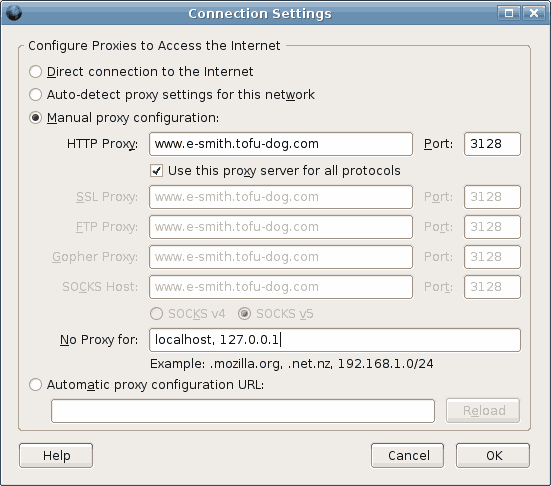
Configuring Your Web Browser
Most browsers (Internet Explorer, Firefox etc) are configured using a dialog box called "preferences", "network preferences" or "options". Some browsers need to be configured to access the Internet either directly or via a proxy server. When required, most desktop applications, your web browser included, should be configured as though they were directly accessing the Internet. Although the server uses a security feature known as IP masquerading, thereby creating an indirect connection to the Internet, this is a transparent operation to most of your desktop applications. Hence, you should ensure that the "Direct connection to the Internet" check box is clicked "on" in your web browser.
Under certain circumstances, using a proxy server can improve the perceived performance of your network. The server includes HTTP, FTP and Gopher proxy servers. Normally, we recommend these be disabled in your browser.
If you decided that you do want to use proxy servers #3, you will need to enter the IP address or domain name of the proxy server (i.e. your server) into the configuration screens of your web browser. The port number you will need to enter to connect to the proxy server is 3128. This information is the same for HTTP, Gopher and FTP proxying. Alternatively your browser can find the proxy details for itself by entering http://proxy/proxy.pac into Automatic proxy configuration URL:
The image below shows how a proxy server would be configured in Mozilla Firefox.
#3 Note that laptop users should disable proxy servers when working away from their local area networks.