Difference between revisions of "Docker design concept"
| (5 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{WIP box}} | {{WIP box}} | ||
| + | {{Note box|Various configuration entries may be deprecated}} | ||
| + | |||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
[[File:Docker_design_conceptv0.1.png]] | [[File:Docker_design_conceptv0.1.png]] | ||
| Line 25: | Line 27: | ||
a CPAN perl library for managing images and containers | a CPAN perl library for managing images and containers | ||
http://search.cpan.org/~alambike/Eixo-Docker-1.103/lib/Eixo/Docker.pod | http://search.cpan.org/~alambike/Eixo-Docker-1.103/lib/Eixo/Docker.pod | ||
| + | |||
| + | https://github.com/alambike/eixo-docker | ||
The Eixo library interacts with Docker API via a TCP socket. By default Docker starts without a TCP socket attached, so we have to add it to the Docker service arguments in /etc/sysconfig/docker. The default port via which the Docker API communicates is 4243 but it can be any port. Below is an example /etc/sysconfig/docker file: | The Eixo library interacts with Docker API via a TCP socket. By default Docker starts without a TCP socket attached, so we have to add it to the Docker service arguments in /etc/sysconfig/docker. The default port via which the Docker API communicates is 4243 but it can be any port. Below is an example /etc/sysconfig/docker file: | ||
| Line 33: | Line 37: | ||
# to the arguments list passed to docker -d | # to the arguments list passed to docker -d | ||
| − | other_args="-g /home/e-smith/files/docker-H 127.0.0.1:4243 -d" | + | other_args="-g /home/e-smith/files/docker -H 127.0.0.1:4243 -d" |
==Options== | ==Options== | ||
| Line 49: | Line 53: | ||
===B. Docker options=== | ===B. Docker options=== | ||
* TBA | * TBA | ||
| + | * Docker cluster?? (Multiple SME Servers load balancing docker containers) | ||
| + | |||
===C. Image options=== | ===C. Image options=== | ||
* Linked containers | * Linked containers | ||
| + | |||
| + | To inspect an image and with what (networking) options it was constructed, one can inspect the image by: | ||
| + | docker inspect [imagename] | ||
==SME Databases== | ==SME Databases== | ||
===Container options=== | ===Container options=== | ||
| + | Container options can be passed to the container at 'boot' time. These options can include the following aspects: | ||
| + | * network (ports, port mapping) | ||
| + | * 'cpu' (load) | ||
| + | * memory allocated (size) | ||
| + | * Storage (mount paths, both inside container and (remote) host) | ||
| + | * Domain names (FQDN (sub)domains, Web server Aliases) | ||
| + | * Links to other containers (container wordpress automatically starts container MySQL) | ||
| + | |||
| + | Unlike containers, images themselves do not carry this information, but only the exposed (open) ports. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Hence the usage of SME Server db system to store preferred options per container. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
Syntax: | Syntax: | ||
db docker_containers [name] | db docker_containers [name] | ||
| Line 138: | Line 160: | ||
'''Install docker to your sme, be aware that you have to do it on a SME9 64 bit''' | '''Install docker to your sme, be aware that you have to do it on a SME9 64 bit''' | ||
| + | original script : https://github.com/docker/docker/blob/master/contrib/mkimage-yum.sh | ||
Create your repository file and save it to /root/repo_file | Create your repository file and save it to /root/repo_file | ||
Latest revision as of 13:26, 22 November 2022
Purpose
This page holds a conceptual design for Docker on SME Server. See more details on Docker here
Overview
Design principles
- This design concept only addresses demonized containers and not interactive containers.
- This design only addresses containers that hold application(s) for end users. Not for sys admins.
- Transparent 'Click to run' user experience
- No integration with Server Manager (Yet).
- Full integration in SME Sever templating system and SME Server db databases
- Pre-build images are not available yet
- No build-in pre-checks regarding starting a container and server capacity
- The design is intended for a single SME Server host, not a cluster or a farm.
- May not effect or compromise default SME Server functionality, stability and security
Resources
Possible resources and tools that can be used:
Eixo::Docker perl library
a CPAN perl library for managing images and containers
http://search.cpan.org/~alambike/Eixo-Docker-1.103/lib/Eixo/Docker.pod
https://github.com/alambike/eixo-docker
The Eixo library interacts with Docker API via a TCP socket. By default Docker starts without a TCP socket attached, so we have to add it to the Docker service arguments in /etc/sysconfig/docker. The default port via which the Docker API communicates is 4243 but it can be any port. Below is an example /etc/sysconfig/docker file:
# /etc/sysconfig/docker # # Other arguments to pass to the docker daemon process # These will be parsed by the sysv initscript and appended # to the arguments list passed to docker -d other_args="-g /home/e-smith/files/docker -H 127.0.0.1:4243 -d"
Options
This document does not address any integration with Server Manager. All input is to be considered a flat file or manual db entries.
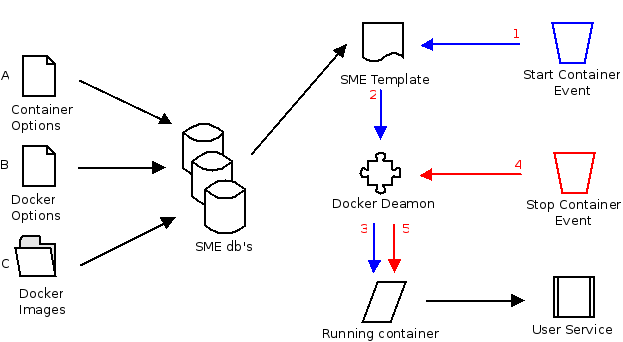
A. Container Options
Start
The docker client can be invoked with various flags and arguments. These flags and arguments are past to the docker daemon to construct the docker container and run it. To see all docker client command execute:
docker
To see all available arguments, execute
docker -h
B. Docker options
- TBA
- Docker cluster?? (Multiple SME Servers load balancing docker containers)
C. Image options
- Linked containers
To inspect an image and with what (networking) options it was constructed, one can inspect the image by:
docker inspect [imagename]
SME Databases
Container options
Container options can be passed to the container at 'boot' time. These options can include the following aspects:
- network (ports, port mapping)
- 'cpu' (load)
- memory allocated (size)
- Storage (mount paths, both inside container and (remote) host)
- Domain names (FQDN (sub)domains, Web server Aliases)
- Links to other containers (container wordpress automatically starts container MySQL)
Unlike containers, images themselves do not carry this information, but only the exposed (open) ports.
Hence the usage of SME Server db system to store preferred options per container.
Syntax:
db docker_containers [name]
Key:
docker_containers [name]=service
Types:
| status | enabled / disabled |
| TCPPort | n , n |
| UDPPort | n , n |
| PortMapping | native / custom |
| PortMappingPorts | n:n , n:n |
| access | private / public |
| network | bridge / host |
| MountPath | path , path |
| Interlinked | [alias] |
| InterLinkPriority | n |
| MaxMemory | n |
| SubDomain | enabled / disabled |
| SubDomainName | name |
| WebAlias | name |
| DataMount | container / host |
| DataMountWrite | yes / no |
| DataMountPath | path |
Image options
Syntax:
db docker_images
Key:
docker_images [name]=service
SME Template/fragments
- TBA
Start/Stop events
- Manual on console
- Time based by cron
- Triggered by an event
Create a SME docker Base image
WIP --Stephdl (talk) 15:56, 15 September 2014 (MDT)
Install docker to your sme, be aware that you have to do it on a SME9 64 bit original script : https://github.com/docker/docker/blob/master/contrib/mkimage-yum.sh
Create your repository file and save it to /root/repo_file
#------------------------------------------------------------ # !!DO NOT MODIFY THIS FILE!! # # Manual changes will be lost when this file is regenerated. # # Please read the developer's guide, which is available # at http://www.contribs.org/development/ # # Copyright (C) 1999-2006 Mitel Networks Corporation #------------------------------------------------------------ [base] enabled=1 mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=6&arch=x86_64&repo=os name=CentOS - os gpgcheck=0 enablegroups=1 exclude=initscripts libgsf [centosplus] enabled=0 mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=centosplus name=CentOS - centosplus gpgcheck=0 enablegroups=0 [contrib] enabled=0 mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=contrib name=CentOS - contrib gpgcheck=0 enablegroups=0 [extras] enabled=0 mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=extras name=CentOS - extras gpgcheck=0 enablegroups=0 [fasttrack] enabled=0 mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=fasttrack name=CentOS - fasttrack gpgcheck=0 enablegroups=0 [smeaddons] enabled=1 mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.contribs.org/mirrorlist/smeaddons-9 name=SME Server - addons gpgcheck=0 enablegroups=1 [smecontribs] enabled=0 mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.contribs.org/mirrorlist/smecontribs-9 name=SME Server - contribs gpgcheck=0 enablegroups=1 [smedev] enabled=0 mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.contribs.org/mirrorlist/smedev-9 name=SME Server - dev gpgcheck=0 enablegroups=1 [smeextras] enabled=1 mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.contribs.org/mirrorlist/smeextras-9 name=SME Server - extras gpgcheck=0 enablegroups=1 [smeos] enabled=1 mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.contribs.org/mirrorlist/smeos-9 name=SME Server - os gpgcheck=0 enablegroups=1 [smetest] enabled=0 mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.contribs.org/mirrorlist/smetest-9 name=SME Server - test gpgcheck=0 enablegroups=1 [smeupdates] enabled=1 mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.contribs.org/mirrorlist/smeupdates-9 name=SME Server - updates gpgcheck=0 enablegroups=1 [smeupdates-testing] enabled=0 mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.contribs.org/mirrorlist/smeupdates-testing-9 name=SME Server - updates testing gpgcheck=0 enablegroups=1 [updates] enabled=1 mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=6&arch=x86_64&repo=updates name=CentOS - updates gpgcheck=0 enablegroups=1 exclude=initscripts libgsf
- first create a file and record the content
vim /root/docker_images
#!/usr/bin/env bash
#
# Create a base CentOS Docker image.
#
# This script is useful on systems with yum installed (e.g., building
# a CentOS image on CentOS). See contrib/mkimage-rinse.sh for a way
# to build CentOS images on other systems.
usage() {
cat <<EOOPTS
$(basename $0) [OPTIONS] <name>
OPTIONS:
-y <yumconf> The path to the yum config to install packages from. The
default is /etc/yum.conf.
EOOPTS
exit 1
}
# option defaults
yum_config=/etc/yum.conf
while getopts ":y:h" opt; do
case $opt in
y)
yum_config=$OPTARG
;;
h)
usage
;;
\?)
echo "Invalid option: -$OPTARG"
usage
;;
esac
done
shift $((OPTIND - 1))
name=$1
if -z $name ; then
usage
fi
#--------------------
target=$(mktemp -d --tmpdir $(basename $0).XXXXXX)
set -x
mkdir -m 755 "$target"/dev
mknod -m 600 "$target"/dev/console c 5 1
mknod -m 600 "$target"/dev/initctl p
mknod -m 666 "$target"/dev/full c 1 7
mknod -m 666 "$target"/dev/null c 1 3
mknod -m 666 "$target"/dev/ptmx c 5 2
mknod -m 666 "$target"/dev/random c 1 8
mknod -m 666 "$target"/dev/tty c 5 0
mknod -m 666 "$target"/dev/tty0 c 4 0
mknod -m 666 "$target"/dev/urandom c 1 9
mknod -m 666 "$target"/dev/zero c 1 5
#yum -c "$yum_config" --installroot="$target" --setopt=tsflags=nodocs \
#--setopt=group_package_types=mandatory -y groupinstall Core
###here it is for testing purpose, you will build a pure centos base docker image (keep only one yum line of course)
#yum -c "/root/repo_file" --installroot="$target" --setopt=tsflags=nodocs --setopt=group_package_types=mandatory -y groupinstall Core ###this line is to test and build a pure centos base in order to test
###with the line below we take all from smeos, not really uptodate
#yum -c "/root/repo_file" --installroot="$target" --setopt=tsflags=nodocs --setopt=group_package_types=mandatory -y install --disablerepo=* --enablerepo=smeos,smeextras e-smith\* smeserver\*
###here we take rpm in the most uptodate version
yum -c "/root/repo_file" --installroot="$target" --setopt=tsflags=nodocs --setopt=group_package_types=mandatory -y install e-smith\* smeserver\*
###a bit of clean
yum -c "/root/repo_file" --installroot="$target" -y clean all
cat > "$target"/etc/sysconfig/network <<EOF
NETWORKING=yes
HOSTNAME=localhost.localdomain
EOF
# effectively: febootstrap-minimize --keep-zoneinfo --keep-rpmdb
# --keep-services "$target". Stolen from mkimage-rinse.sh
# locales
rm -rf "$target"/usr/{{lib,share}/locale,{lib,lib64}/gconv,bin/localedef,sbin/build-locale-archive}
# docs
rm -rf "$target"/usr/share/{man,doc,info,gnome/help}
# cracklib
rm -rf "$target"/usr/share/cracklib
# i18n
rm -rf "$target"/usr/share/i18n
# sln
rm -rf "$target"/sbin/sln
# ldconfig
rm -rf "$target"/etc/ld.so.cache
rm -rf "$target"/var/cache/ldconfig/*
#version=
if [ -r "$target"/etc/redhat-release ]; then
version="$(sed 's/^[^0-9\]*\([0-9.]\+\).*$/\1/' "$target"/etc/redhat-release)"
fi
if [ -z "$version" ]; then
echo >&2 "warning: cannot autodetect OS version, using '$name' as tag"
version=$name
fi
tar --numeric-owner -c -C "$target" . | docker import - $name:$version
docker run -i -t $name:$version echo success
rm -rf "$target"
give the permissions to the file
chmod u+x /root/docker_images
and launch the script
/root/docker_images [name_of_your_image]
you have to wait, the download depends of your bandwith, once done you could see 'success'
docker run -i -t sme9_real:6.5 echo success success
to launch your image
docker run -i -t sme9_real:6.5 bash
see
docker images
after that you have an image but we need to reconfigure it