Difference between revisions of "VirtualBox 4.0 on SME Server v8 beta 6"
Unnilennium (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (90 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{warning box|this how to is out of date. You probably wants to install the smeserver-phpvirtualbox and smeserver-virtualbox contribs for SME8 and SME9, then see here : [[Phpvirtualbox]]}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Maintainer=== | ||
| + | [http://www.compsos.com.au CompSOS] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Support=== | ||
| + | For questions or comments regarding this HOWTO, contact [mailto:shiena@compsos.com.au Shiena] of [http://www.compsos.com.au Computing SOS] or Sorolo Systems Inc. at this [mailto:sme@sorolo.com email] address. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Description=== | ||
| + | Below are instructions on how to install VirtualBox version 4.1 on a fresh install SME Server v8 beta 6 and higher. Plus installing and configuring phpVirtualBox to control (create, edit, remove) your virtual machine on its web interface. In addition, scripts to automatically start the vbox service and the virtual machines in case of power failure can be found at the end of this article. | ||
| + | |||
| + | This has been tested using the following:<br/> | ||
<ol> | <ol> | ||
| − | <li>Setup SME Server v8 | + | <li>SME Server Release 8.0</li> |
| − | <li> | + | <li>VirtualBox-4.3</li> |
| + | <li>Kernel is 2.6.18-348.6.1.el5</li> | ||
| + | </ol> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Requirements=== | ||
| + | Computer with SME server version 8 and higher installed. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Installation=== | ||
| + | <ol> | ||
| + | <li value="1">Setup SME Server v8.</li> | ||
| + | <li value="2">Do a yum update.</li> | ||
| + | <pre>yum upgrade</pre> | ||
| + | <li value="3"> If any updates were applied, update and reboot the server.</li> | ||
| + | <pre>signal-event post-upgrade; signal-event reboot</pre> | ||
| + | <li value="4">Check your current kernel.</li> | ||
| + | <pre>uname -r</pre> | ||
| + | <li value="5">Install kernel-devel to get the latest development tree.<br/> | ||
| + | Use the command below, only if you have a PAE kernel installed: | ||
| + | <pre>yum clean all | ||
| + | yum install kernel-PAE-devel kernel-headers | ||
| + | yum info kernel-headers</pre> | ||
| + | Otherwise, | ||
| + | <pre>yum install kernel-devel kernel-headers</pre> | ||
| + | </li> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Note : if you do not want to update your kernel, because of kmdl not available you can search for the right kernel-headers and kernel-devel in http://vault.centos.org/ | ||
| + | |||
| + | <li value="6">Check if the compiler (GCC) is installed by issuing this command. | ||
| + | <pre>rpm -qa | grep gcc</pre> | ||
| + | You will have an output, similar to this: | ||
| + | <pre>libgcc-4.1.2-54.el5 | ||
| + | gcc-4.1.2-54.el5</pre> | ||
| + | If not installed, install it. | ||
| + | <pre>yum install gcc</pre> | ||
| + | If you will get an error "No package gcc available. Nothing to do" then do this: | ||
| + | <pre>cd /tmp | ||
| + | wget ftp://ftp.mirrorservice.org/sites/sourceware.org/pub/gcc/releases/gcc-4.7.1/gcc-4.7.1.tar.gz</pre> | ||
| + | </li> | ||
| + | <li value="7">Update SME, and reboot again.</li> | ||
| + | <pre>signal-event post-upgrade; signal-event reboot</pre> | ||
| + | <li value="8">Change your kernel boot options.<br/> | ||
| + | Optionally, for best results with SME 8.x and earlier versions, modify /etc/grub.conf, adding divider=10 to the kernel boot options in order | ||
| + | to reduce the idle CPU load with VirtualBox. For example, if your kernel boot line is: | ||
| + | <pre>kernel /vmlinuz-2.6.18-348.6.1.el5 ro root=/dev/main/root </pre> | ||
| + | <p>change it to:</p> | ||
| + | <pre>kernel /vmlinuz-2.6.18-348.6.1.el5 ro root=/dev/main/root divider=10</pre> | ||
| + | <p><b>Reminder:</b> if you subsequently update SME Server to use a newer kernel, you may need to change | ||
| + | your kernel boot line to reflect the update.</p> | ||
| + | </li> | ||
| + | <li value="9">Create a symbolic link.<br/> | ||
| + | <p><b>NOTE:</b> Be careful if you cut-and-paste the command below. <!--In some terminal windows, from some browsers, the parts of the command in | ||
| + | bold font do not paste correctly.-->Pay particular attention to the dashes (-) and the backticks (`). There aren't any single quote marks in | ||
| + | the command below - they are all supposed to be backticks.</p> | ||
| + | <pre>ln -s /usr/src/kernels/`uname -r`-`uname -m` /lib/modules/`uname -r`/build</pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><b>Reminder:</b> if you subsequently update SME Server to use a newer kernel, you may need to recreate the symbolic link.</p> | ||
| + | </li> | ||
| + | <li value="10">Check that the symbolic link was properly created by doing a directory listing.<br/> | ||
| + | <p><b>NOTE:</b> Be careful if you cut-and-paste the command below. In some terminal windows, from some browsers, the parts of the command in | ||
| + | bold font do not paste correctly. Pay particular attention to the dashes (-) and the backticks (`). There aren't any single quote marks in | ||
| + | the command below - they are all supposed to be backticks.</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <pre>ls -la /lib/modules/`uname -r`/build</pre> | ||
| + | </li> | ||
| + | <li value="11">Install the Fedora Epel repository using the instructions [http://wiki.contribs.org/Epel here].</li> | ||
| + | <li value="12">Install Dynamic Kernel Module Support (DKMS)</li> | ||
| + | <pre>yum install --enablerepo=epel dkms</pre> | ||
| + | <li value="13">Install the VirtualBox repository using the instructions [http://wiki.contribs.org/VirtualBox_Repository here].</li> | ||
| + | <li value="14">Install <b>VirtualBox</b> (At the time of the last update to these instructions, the latest version was v4.3-4.3.6-91406).</li> | ||
| + | <pre>yum install --enablerepo=virtualbox VirtualBox-4.3</pre> | ||
| + | <li value="15">Review the VirtualBox installation log to ensure that the installation was successful.</li> | ||
| + | <pre>tail /var/log/vbox-install.log</pre> | ||
| + | <li value="16">Remove the compiler install (for security best practices)</li> | ||
| + | <pre>rpm -e gcc</pre> | ||
| + | <li value="17">Update SME, and reboot again</li> | ||
| + | <pre>signal-event post-upgrade; signal-event reboot</pre> | ||
| + | <li value="18">Setup VirtualBox as a service so it starts automatically after a reboot. Copy the command below on putty console then hit Enter.</li> | ||
| + | <pre>for file in $(ls /etc/rc5.d/S??vbox*); do cp "$file" /etc/rc7.d/. ;done</pre> | ||
| + | <li value="19">Create a ''virtualbox'' file on your /etc/default/.</li> | ||
| + | <pre>nano /etc/default/virtualbox</pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | virtualbox should have this content. | ||
| + | <pre>VBOXWEB_USER='root' | ||
| + | VBOXWEB_HOST=127.0.0.1 | ||
| + | VBOXWEB_PORT=18083 | ||
| + | VBOXWEB_LOGFILE=/var/log/vboxweb | ||
| + | INSTALL_DIR=/usr/lib/virtualbox</pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <b>Note: Without the ''virtualbox'' file, vbox services on your rc7.d folder will not start.</b> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <li value="20">Install phpVirtualBox using this link http://wiki.contribs.org/Phpvirtualbox#DB_Configuration | ||
| − | + | <li value="21">Ensure that the extension pack is installed correctly. | |
| − | + | Open a console window, then | |
| − | + | <pre>vboxmanage list extpacks</pre> | |
| + | </li> | ||
| + | At this point, VirtualBox should now be configured and running correctly. To check this, we will now log into the ibay we created for phpVirtualBox and attempt to create a new virtual machine. If you encounter problems, please recheck that you have setup VirtualBox as a service so it starts automatically after a reboot, and that your vbox.cfg file is configured correctly. To manage VirtualBox and any virtual machines, use the command line utility VBoxManage. See VBoxManage --help . For a list of available switches for VBoxManage, see [http://www.virtualbox.org/manual/ch08.html this list]. | ||
| − | <li> | + | Finally, |
| + | |||
| + | <li value="22">Open a terminal window to the SME Server and create a directory to store the virtual machine images.</li> | ||
| + | <pre>mkdir -p /root/VirtualBox VMs/addons</pre> | ||
| + | <li value="23">Download the VirtualBox Guest Additions iso for later installation into your virtual machine guests.</li> | ||
| + | <pre>cd /root/VirtualBox VMs/addons | ||
| + | wget http://download.virtualbox.org/virtualbox/4.3.6/VBoxGuestAdditions_4.3.6.iso</pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <li value="24">Using a web browser, Go to http://yourdomain.com/phpvirtualbox and connect to the phpVirtualBox web application. | ||
| + | At this point, VirtualBox should now be configured and running correctly. If you encounter problems, please recheck that you have setup VirtualBox as a service so it starts automatically after a reboot, and that your vbox.cfg file is configured correctly. To manage VirtualBox and any virtual machines, use the command line utility VBoxManage. See VBoxManage --help . For a list of available switches for VBoxManage, see this list. | ||
| + | </li> | ||
| + | |||
| + | </ol> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Creating a Virtual Machine=== | ||
| + | <ol> | ||
| + | <li>Using a web browser, go to http://yourdomain.com/phpvirtualbox to create your virtual machine. | ||
| + | <ul> | ||
| + | <li>Create a new virtual machine (e.g. vmXP)</li> | ||
| + | <li>Enable network card (either NAT or Bridged) so you can connect to your new VM console.</li> | ||
| + | </ul> | ||
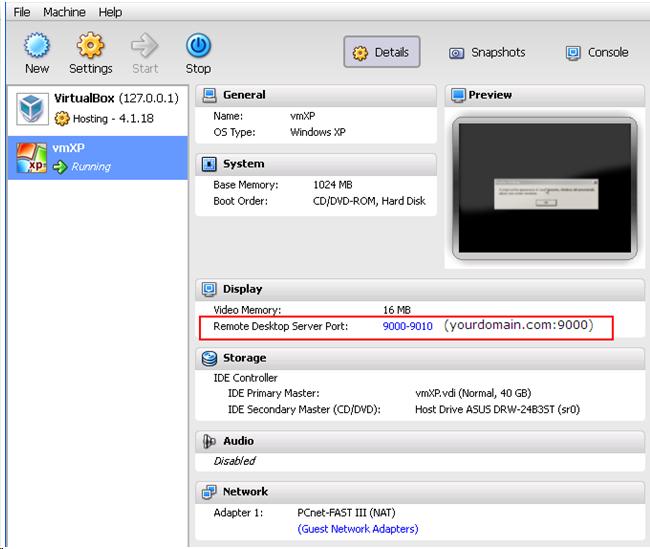
| + | [[File:PhpVirtualBox-rdp-port.jpg]] | ||
| + | <li>Even when the extension is installed, the VRDP server is disabled by default. On console:</li> | ||
| + | <pre>vboxmanage modifyvm "vmXP" --vrde on</pre> | ||
| + | <li>Ensure you are connected to the server's internal network, then open a Remote Desktop client program. | ||
| + | <ul> | ||
| + | <li>On Windows, open an RDP client (run -> mstsc) then type your server’s hostname:port number (e.g. myserver:9000), or your Server's (not your Guest) IP address followed by colon then the port number as shown on above image (Remote Desktop Server Port under Display) (e.g. 192.168.100.1:9000).</li> | ||
| + | <b>NOTE:</b> No need to change to port number to 9000 (as per above) in your Windows registry (HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\TerminalServer\WinStations\RDP-Tcp\PortNumber). It will still be using port 3389 even though phpVirtualBox is using port 9000.<br/> | ||
| + | If you're remotely connected to your server's phpvirtualbox and adding a new Guest remotely, open port 9000 (source and destination TCP poty) pointing to server's IP, so you can be able to access the console built-in to PhpVirtualBox. | ||
| + | </li> | ||
| + | </ul> | ||
| + | <li>Install the VirtualBox Guest Additions ISO into your newly setup VM.</li> | ||
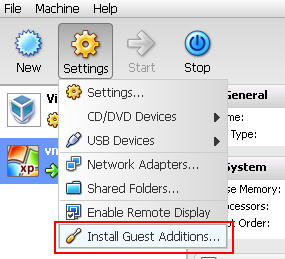
| + | [[File:PhpVirtualBox-install-guest-addition.jpg]] | ||
| + | </ol> | ||
| − | + | ===Access VM outside the Network=== | |
| + | <ol> | ||
| + | <li>On SME Server Manager page, on <b>Port Forwarding</b> left menu, open port <b>9000</b> (as per Remote Desktop Server Port under Display) using your desired Source Port:</li> | ||
| + | Protocol: TCP<br/> | ||
| + | Source Ports: 33900<br/> | ||
| + | Destination IP: 192.168.5.1 ''(which is also the guest IP'')<br/> | ||
| + | Destination Port: 9000<br/> | ||
| + | Allow Hosts: <you can leave it blank, or place your Public IP so only your IP can access the VM)<br/> | ||
| + | Rule Comment: <eg. vmXP for SOS><br/> | ||
| + | <li>Now you can access your VM thru RDP using this hostname ''domain.com:33900''</li> | ||
| + | </ol> | ||
| − | + | ===Automatically Start Virtual Machine=== | |
| − | + | <ol> | |
| − | + | <!--<li>Create a file (e.g. startXP) on /etc/init.d/</li> | |
| − | + | <pre>nano /etc/init.d/startXP</pre> | |
| − | + | startXP code should look like this: | |
| + | <pre>vboxmanage startvm --type headless vmXP</pre> | ||
| + | --> | ||
| + | <li>Edit your <b>vbox</b> file on /etc/sysconfig/</li> | ||
| + | <pre>nano /etc/sysconfig/vbox</pre> | ||
| + | vbox code should look like this: | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | # Virtual box machines to autostart | ||
| + | # Example to start 2 machines | ||
| + | # VBOX_AUTOSTART = "MachineName1 MachineName2" | ||
| + | VBOX_AUTOSTART="vmXP" | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| − | + | <li>Edit your ''vbox'' file located on /etc/init.d/ | |
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | #!/bin/sh | ||
| + | # | ||
| + | # chkconfig: - 91 35 | ||
| + | # description: Starts and stops vbox autostart VMs. | ||
| − | + | ### BEGIN INIT INFO | |
| + | # Provides: vbox | ||
| + | # Required-Start: $network $named $vboxdrv | ||
| + | # Required-Stop: $network $named | ||
| + | # Default-Start: | ||
| + | # Default-Stop: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 | ||
| + | # Short-Description: Autostart some Virtual Box VMs | ||
| + | # Description: Autostart some Virtual Box VMs that are mentioned in /etc/sysconfig/vbox file | ||
| + | # Written by Alex Amiryan | ||
| + | ### END INIT INFO | ||
| − | + | . /etc/rc.d/init.d/functions | |
| − | + | MANAGE_CMD=vboxmanage | |
| − | + | [ -r /etc/sysconfig/vbox ] && . /etc/sysconfig/vbox | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | prog=$"Virtual Box Machines" | |
| − | |||
| − | + | start() | |
| − | + | { | |
| − | + | echo -n $"Starting $prog: " | |
| − | + | RETVAL=0 | |
| − | + | for vbox_name in ${VBOX_AUTOSTART} | |
| − | + | do | |
| − | + | SERVS=1 | |
| − | + | echo -n "${vbox_name} " | |
| + | daemon $MANAGE_CMD startvm "${vbox_name}" -type headless >/dev/null 2>&1 | ||
| + | RETVAL=$? | ||
| + | [ "$RETVAL" -eq 0 ] || break | ||
| + | done | ||
| + | if [ -z "$SERVS" ]; then | ||
| + | echo -n "no virtual machines configured " | ||
| + | failure | ||
| + | RETVAL=6 | ||
| + | else | ||
| + | if [ "$RETVAL" -eq 0 ]; then | ||
| + | success $"vbox startup" | ||
| + | touch /var/lock/subsys/vbox | ||
| + | else | ||
| + | failure $"vbox start" | ||
| + | fi | ||
| + | fi | ||
| + | echo | ||
| + | return "$RETVAL" | ||
| + | } | ||
| − | + | stop() | |
| − | + | { | |
| + | echo -n $"Shutting down $prog: " | ||
| + | for vbox_name in ${VBOX_AUTOSTART} | ||
| + | do | ||
| + | echo -n "${vbox_name} " | ||
| + | runuser root -c "$MANAGE_CMD -q controlvm "${vbox_name}" savestate" >/dev/null 2>&1 | ||
| + | done | ||
| + | RETVAL=$? | ||
| + | [ "$RETVAL" -eq 0 ] && success $"vbox shutdown" || \ | ||
| + | failure $"vbox shutdown" | ||
| + | echo | ||
| + | [ "$RETVAL" -eq 0 ] && rm -f /var/lock/subsys/vbox | ||
| + | return "$RETVAL" | ||
| + | } | ||
| − | + | status() | |
| − | + | { | |
| − | + | for vbox_name in ${VBOX_AUTOSTART} | |
| − | + | do | |
| + | echo -n "${vbox_name} " | ||
| + | $MANAGE_CMD showvminfo "${vbox_name}"|grep "^State:\s*.*$" | ||
| + | done | ||
| + | } | ||
| − | + | case "$1" in | |
| − | + | start) | |
| + | start | ||
| + | ;; | ||
| + | stop) | ||
| + | stop | ||
| + | ;; | ||
| + | restart|force-reload) | ||
| + | stop | ||
| + | start | ||
| + | ;; | ||
| + | status) | ||
| + | status | ||
| + | ;; | ||
| + | *) | ||
| + | echo "Usage: $SCRIPTNAME {start|stop|restart|force-reload|status}" >&2 | ||
| + | exit 3 | ||
| + | ;; | ||
| + | esac | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | </li> | ||
| + | </ol> | ||
| − | + | ===Troubleshooting=== | |
| − | |||
| − | <li> | + | <ol> |
| − | <li></ | + | <li><p>PhpVirtualBox throws an error <i>attribute does not exist</i> or <i>method 'getVDENetwork' does not exist in the object</i>.</p> |
| + | <p><b>Solution:</b> Check config.php file located on /home/e-smith/files/ibays/phpvbox/html/ and comment out the line <i>var $enableVDE = true;</i></p> | ||
| + | </li> | ||
| + | <pre>#var $enableVDE = true;</pre> | ||
| + | <li><p>Virtual machine with a guest Windows XP installed takes too long to load.</p> | ||
| + | <p><b>Solution:</b> The Windows XP disk you might have used is slipstreamed with Intel ICH9 or ICH10. Uninstall <i>iastor.sys</i> on Safe Mode. Once you restart, it will reinstall it for you. <i>Iastor.sys</i> is an Intel Matrix storage manager, used to access RAID drives system driver file.</p> | ||
| + | </li> | ||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category: Virtualisation]] | ||
| + | [[Category: Advanced]] | ||
| + | [[Category: Howto]] | ||
Latest revision as of 20:49, 12 March 2017
Maintainer
Support
For questions or comments regarding this HOWTO, contact Shiena of Computing SOS or Sorolo Systems Inc. at this email address.
Description
Below are instructions on how to install VirtualBox version 4.1 on a fresh install SME Server v8 beta 6 and higher. Plus installing and configuring phpVirtualBox to control (create, edit, remove) your virtual machine on its web interface. In addition, scripts to automatically start the vbox service and the virtual machines in case of power failure can be found at the end of this article.
This has been tested using the following:
- SME Server Release 8.0
- VirtualBox-4.3
- Kernel is 2.6.18-348.6.1.el5
Requirements
Computer with SME server version 8 and higher installed.
Installation
- Setup SME Server v8.
- Do a yum update.
- If any updates were applied, update and reboot the server.
- Check your current kernel.
- Install kernel-devel to get the latest development tree.
Use the command below, only if you have a PAE kernel installed:yum clean all yum install kernel-PAE-devel kernel-headers yum info kernel-headers
Otherwise,
yum install kernel-devel kernel-headers
Note : if you do not want to update your kernel, because of kmdl not available you can search for the right kernel-headers and kernel-devel in http://vault.centos.org/
- Check if the compiler (GCC) is installed by issuing this command.
rpm -qa | grep gcc
You will have an output, similar to this:
libgcc-4.1.2-54.el5 gcc-4.1.2-54.el5
If not installed, install it.
yum install gcc
If you will get an error "No package gcc available. Nothing to do" then do this:
cd /tmp wget ftp://ftp.mirrorservice.org/sites/sourceware.org/pub/gcc/releases/gcc-4.7.1/gcc-4.7.1.tar.gz
- Update SME, and reboot again.
- Change your kernel boot options.
Optionally, for best results with SME 8.x and earlier versions, modify /etc/grub.conf, adding divider=10 to the kernel boot options in order to reduce the idle CPU load with VirtualBox. For example, if your kernel boot line is:kernel /vmlinuz-2.6.18-348.6.1.el5 ro root=/dev/main/root
change it to:
kernel /vmlinuz-2.6.18-348.6.1.el5 ro root=/dev/main/root divider=10
Reminder: if you subsequently update SME Server to use a newer kernel, you may need to change your kernel boot line to reflect the update.
- Create a symbolic link.
NOTE: Be careful if you cut-and-paste the command below. Pay particular attention to the dashes (-) and the backticks (`). There aren't any single quote marks in the command below - they are all supposed to be backticks.
ln -s /usr/src/kernels/`uname -r`-`uname -m` /lib/modules/`uname -r`/build
Reminder: if you subsequently update SME Server to use a newer kernel, you may need to recreate the symbolic link.
- Check that the symbolic link was properly created by doing a directory listing.
NOTE: Be careful if you cut-and-paste the command below. In some terminal windows, from some browsers, the parts of the command in bold font do not paste correctly. Pay particular attention to the dashes (-) and the backticks (`). There aren't any single quote marks in the command below - they are all supposed to be backticks.
ls -la /lib/modules/`uname -r`/build
- Install the Fedora Epel repository using the instructions here.
- Install Dynamic Kernel Module Support (DKMS)
- Install the VirtualBox repository using the instructions here.
- Install VirtualBox (At the time of the last update to these instructions, the latest version was v4.3-4.3.6-91406).
- Review the VirtualBox installation log to ensure that the installation was successful.
- Remove the compiler install (for security best practices)
- Update SME, and reboot again
- Setup VirtualBox as a service so it starts automatically after a reboot. Copy the command below on putty console then hit Enter.
- Create a virtualbox file on your /etc/default/.
- Install phpVirtualBox using this link http://wiki.contribs.org/Phpvirtualbox#DB_Configuration
- Ensure that the extension pack is installed correctly.
Open a console window, then
vboxmanage list extpacks
At this point, VirtualBox should now be configured and running correctly. To check this, we will now log into the ibay we created for phpVirtualBox and attempt to create a new virtual machine. If you encounter problems, please recheck that you have setup VirtualBox as a service so it starts automatically after a reboot, and that your vbox.cfg file is configured correctly. To manage VirtualBox and any virtual machines, use the command line utility VBoxManage. See VBoxManage --help . For a list of available switches for VBoxManage, see this list.
Finally,
- Open a terminal window to the SME Server and create a directory to store the virtual machine images.
- Download the VirtualBox Guest Additions iso for later installation into your virtual machine guests.
- Using a web browser, Go to http://yourdomain.com/phpvirtualbox and connect to the phpVirtualBox web application. At this point, VirtualBox should now be configured and running correctly. If you encounter problems, please recheck that you have setup VirtualBox as a service so it starts automatically after a reboot, and that your vbox.cfg file is configured correctly. To manage VirtualBox and any virtual machines, use the command line utility VBoxManage. See VBoxManage --help . For a list of available switches for VBoxManage, see this list.
yum upgrade
signal-event post-upgrade; signal-event reboot
uname -r
signal-event post-upgrade; signal-event reboot
yum install --enablerepo=epel dkms
yum install --enablerepo=virtualbox VirtualBox-4.3
tail /var/log/vbox-install.log
rpm -e gcc
signal-event post-upgrade; signal-event reboot
for file in $(ls /etc/rc5.d/S??vbox*); do cp "$file" /etc/rc7.d/. ;done
nano /etc/default/virtualbox
virtualbox should have this content.
VBOXWEB_USER='root' VBOXWEB_HOST=127.0.0.1 VBOXWEB_PORT=18083 VBOXWEB_LOGFILE=/var/log/vboxweb INSTALL_DIR=/usr/lib/virtualbox
Note: Without the virtualbox file, vbox services on your rc7.d folder will not start.
mkdir -p /root/VirtualBox VMs/addons
cd /root/VirtualBox VMs/addons wget http://download.virtualbox.org/virtualbox/4.3.6/VBoxGuestAdditions_4.3.6.iso
Creating a Virtual Machine
- Using a web browser, go to http://yourdomain.com/phpvirtualbox to create your virtual machine.
- Create a new virtual machine (e.g. vmXP)
- Enable network card (either NAT or Bridged) so you can connect to your new VM console.
- Even when the extension is installed, the VRDP server is disabled by default. On console:
- Ensure you are connected to the server's internal network, then open a Remote Desktop client program.
- On Windows, open an RDP client (run -> mstsc) then type your server’s hostname:port number (e.g. myserver:9000), or your Server's (not your Guest) IP address followed by colon then the port number as shown on above image (Remote Desktop Server Port under Display) (e.g. 192.168.100.1:9000). NOTE: No need to change to port number to 9000 (as per above) in your Windows registry (HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\TerminalServer\WinStations\RDP-Tcp\PortNumber). It will still be using port 3389 even though phpVirtualBox is using port 9000.
If you're remotely connected to your server's phpvirtualbox and adding a new Guest remotely, open port 9000 (source and destination TCP poty) pointing to server's IP, so you can be able to access the console built-in to PhpVirtualBox. - Install the VirtualBox Guest Additions ISO into your newly setup VM.
vboxmanage modifyvm "vmXP" --vrde on
Access VM outside the Network
- On SME Server Manager page, on Port Forwarding left menu, open port 9000 (as per Remote Desktop Server Port under Display) using your desired Source Port: Protocol: TCP
- Now you can access your VM thru RDP using this hostname domain.com:33900
Source Ports: 33900
Destination IP: 192.168.5.1 (which is also the guest IP)
Destination Port: 9000
Allow Hosts: <you can leave it blank, or place your Public IP so only your IP can access the VM)
Rule Comment: <eg. vmXP for SOS>
Automatically Start Virtual Machine
- Edit your vbox file on /etc/sysconfig/
- Edit your vbox file located on /etc/init.d/
#!/bin/sh # # chkconfig: - 91 35 # description: Starts and stops vbox autostart VMs. ### BEGIN INIT INFO # Provides: vbox # Required-Start: $network $named $vboxdrv # Required-Stop: $network $named # Default-Start: # Default-Stop: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 # Short-Description: Autostart some Virtual Box VMs # Description: Autostart some Virtual Box VMs that are mentioned in /etc/sysconfig/vbox file # Written by Alex Amiryan ### END INIT INFO . /etc/rc.d/init.d/functions MANAGE_CMD=vboxmanage [ -r /etc/sysconfig/vbox ] && . /etc/sysconfig/vbox prog=$"Virtual Box Machines" start() { echo -n $"Starting $prog: " RETVAL=0 for vbox_name in ${VBOX_AUTOSTART} do SERVS=1 echo -n "${vbox_name} " daemon $MANAGE_CMD startvm "${vbox_name}" -type headless >/dev/null 2>&1 RETVAL=$? [ "$RETVAL" -eq 0 ] || break done if [ -z "$SERVS" ]; then echo -n "no virtual machines configured " failure RETVAL=6 else if [ "$RETVAL" -eq 0 ]; then success $"vbox startup" touch /var/lock/subsys/vbox else failure $"vbox start" fi fi echo return "$RETVAL" } stop() { echo -n $"Shutting down $prog: " for vbox_name in ${VBOX_AUTOSTART} do echo -n "${vbox_name} " runuser root -c "$MANAGE_CMD -q controlvm "${vbox_name}" savestate" >/dev/null 2>&1 done RETVAL=$? [ "$RETVAL" -eq 0 ] && success $"vbox shutdown" || \ failure $"vbox shutdown" echo [ "$RETVAL" -eq 0 ] && rm -f /var/lock/subsys/vbox return "$RETVAL" } status() { for vbox_name in ${VBOX_AUTOSTART} do echo -n "${vbox_name} " $MANAGE_CMD showvminfo "${vbox_name}"|grep "^State:\s*.*$" done } case "$1" in start) start ;; stop) stop ;; restart|force-reload) stop start ;; status) status ;; *) echo "Usage: $SCRIPTNAME {start|stop|restart|force-reload|status}" >&2 exit 3 ;; esac
nano /etc/sysconfig/vbox
vbox code should look like this:
# Virtual box machines to autostart # Example to start 2 machines # VBOX_AUTOSTART = "MachineName1 MachineName2" VBOX_AUTOSTART="vmXP"
Troubleshooting
PhpVirtualBox throws an error attribute does not exist or method 'getVDENetwork' does not exist in the object.
Solution: Check config.php file located on /home/e-smith/files/ibays/phpvbox/html/ and comment out the line var $enableVDE = true;
Virtual machine with a guest Windows XP installed takes too long to load.
Solution: The Windows XP disk you might have used is slipstreamed with Intel ICH9 or ICH10. Uninstall iastor.sys on Safe Mode. Once you restart, it will reinstall it for you. Iastor.sys is an Intel Matrix storage manager, used to access RAID drives system driver file.
#var $enableVDE = true;