Difference between revisions of "SharedFolders"
m (→Description) |
|||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
=== Description === | === Description === | ||
| − | + | Shared folders are more or less like ibays (I took a lot of code from the ibay module), but with more flexibility on file permissions as it supports ACL. There're also some additional options in the panel. | |
=== Requirements === | === Requirements === | ||
Revision as of 18:02, 5 July 2011
Maintainer
Daniel B.
Firewall Services
mailto:daniel@firewall-services.com
Version
Description
Shared folders are more or less like ibays (I took a lot of code from the ibay module), but with more flexibility on file permissions as it supports ACL. There're also some additional options in the panel.
Requirements
- SME Server 7.X
Installation
- install the rpms
yum --enablerepo=smecontribs install smeserver-shared-folders
- Mount your file system(s) with the ACL option
If you use a standard SME server installation:
signal-event post-upgrade && signal-event reboot
should do the trick. If you don't like to reboot your server every time you install something (just like me :)), you can just run:
expand-template /etc/fstab
Check your file system mounted in /home/e-smith/files/ has the acl option, for example:
# This file is edited by fstab-sync - see 'man fstab-sync' for details LABEL=/ / ext3 usrquota,grpquota,acl 1 1 LABEL=/boot /boot ext3 defaults 1 2 none /dev/pts devpts gid=5,mode=620 0 0 none /dev/shm tmpfs defaults 0 0 none /proc proc defaults 0 0 none /sys sysfs defaults 0 0 LABEL=SWAP-rd/c0d0p3 swap swap defaults 0 0
You may have to manually add the acl option in /etc/fstab if you have mounted another file system here. Once the option is in fstab, you can just remount the partitions, for example:
mount -o remount /
or
mount -o remount /home/e-smith/files
Check everything is ok:
[root@sme ~]# mount /dev/sda2 on / type ext3 (rw,usrquota,grpquota,acl) none on /proc type proc (rw) none on /sys type sysfs (rw) none on /dev/pts type devpts (rw,gid=5,mode=620) usbfs on /proc/bus/usb type usbfs (rw) /dev/rd/c0d0p1 on /boot type ext3 (rw) none on /dev/shm type tmpfs (rw) none on /proc/sys/fs/binfmt_misc type binfmt_misc (rw)
Storage
All the shares you create will be stored in /home/e-smith/files/shares/<sharename>/files The latest /files directory is to keep the same structure than ibays. There's no html and cgi-bin directories. You'll never see the "files" directory as the root (for SMB and HTTP) will always be /home/e-smith/files/shares/<sharename>/files.
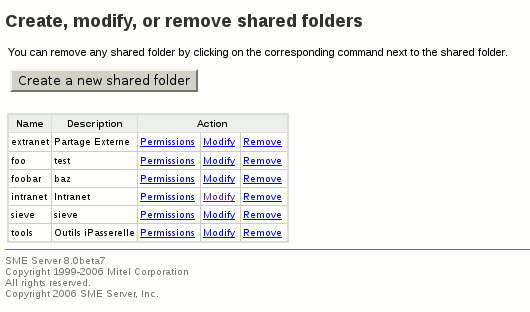
Screenshots
Features
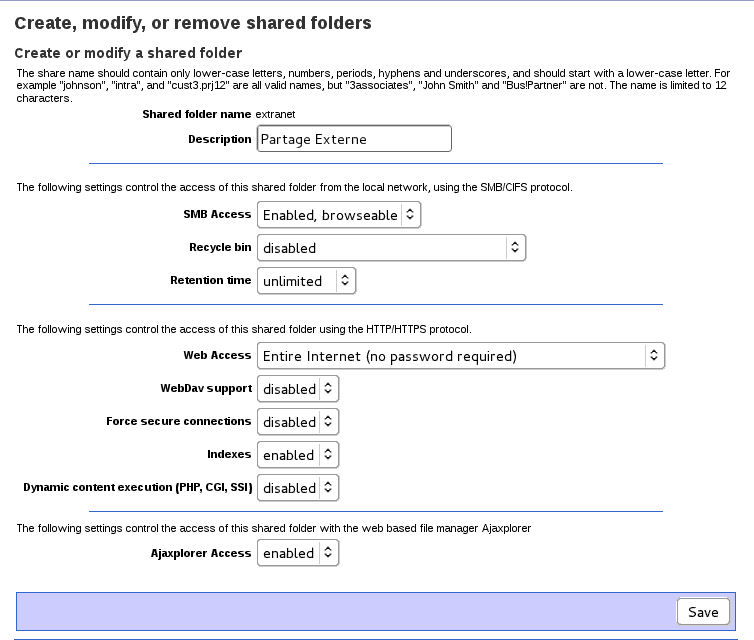
A lot of options are available in the panel. When you create a new shared folder, or modify an existing one, the page is divided in 4 parts:
- The first part let you enter a name and a comment for this shared folder. This part works exactly the same way than ibay. An initial limit of 12 characters exists for the name. You can raise this value with
db configuration set maxShareNameLength 16
- The second part is to define permission access. For each group of users, you can grant read only or read/write access. If none is checked, the shared folder won't be accessible (unless for the admin user which has always access to every shared folders)
- The third part let you configure access to this shared folder using the SMB/CIFS protocol. There's two drop down menu
- SMB Access lets you configure the type of access: none (no access), enabled and browseable (enabled, and visible if you browse available shares of the server) or enabled, hidden (enabled, but you need to know the exact name to access it)
- Recycle bin lets you configure a network recycle bin option available in samba. Available options are none (recycle bin is disabled), enabled, keep only the latest version (enable the recycle bin, but only keep the latest version if two file with the same name are deleted), or enabled, keep a copy of all versions (enable the recycle bin and keep a copy of every file deleted). When the recycle bin is enabled, if a user delete a file, instead of removing it from the server, samba will move it the the Recycle Bin directory at the top of the shared folder (the directory is created if it doesn't exist)
- The fourth part let you configure access to this shared folder using the HTTP/HTTPS protocol. There're also several options:
- Web Access: works like ibays. The only difference is that when a password is required, users have to use their own login/password instead of a global one. Users need at least read access to this share or they won't be allowed. This setting is only for web access, not FTP.
- WebDav Support: Enable webdav on this share. Only effective if Web Access is enabled with a password.
- Force secure connections: if enabled, all the requests will be redirected to use the HTTPS protocol. The redirection is transparent.
- Indexes: Let you control if the server should generate an index of all the files if no index.html file is found. You can disable it if you don't want everyone to have access to the list of files. This setting is global for the shared folder, I mean, if enabled, any directory which doesn't have a index.html file will be indexed.
- Dynamic content execution (PHP, CGI, SSI): this enable the execution of PHP script. If disabled files with php, php3, phtml, cgi or pl as extension won't be allowed. If enabled, you can create a directory named "cgi-bin" in your shared folder. It will allow execution of cgi scripts
Additional options
Some advanced settings are not available on the panel, but only with db commands:
- Various options
- ManualPermissions: if you set this key to enabled, the panel wont show the permission matrix, and permissions won't be reseted if you modify this shared folder. This can be used to host web application with custom permissions.
- Options for Web access:
- AllowOverride: You can configure the AllowOverride directive of apache if web access is enabled. See this page for a list of available option
- FollowSymLinks: (enabled|disabled). Should apache follows symlinks ?
- PHPRegisterGlobals: (enabled|disabled). Enable PHP register global for this share.
- PHPAllowUrlFopen: (enabled|disabled). Enable PHP allow_url_fopen for this share.
- PHPMemoryLimit: Set a memory limit for PHP. This limit only apply to this share
- PHPMaxExecutionTime: Set a time execution limit for PHP. This limit only apply to this share
- Options for SMB access:
- cscPolicy: (disabled|manual|documents|programs). Control client-side caching. Don't touch this if you don't know what it means. It can have unexpected behaviour.
- OpLocks: (enabled|disabled). Control the oplocks option of samba (default is enabled)
- VetoOplockFiles: Control the veto oplock files of samba
Example:
db accounts setprop myshare AllowOverride All PHPMemoryLimit 50M PHPMaxExecutionTime 600 signal-event share-modify myshare
Missing features
Even if this contrib brings some new options compared to ibays, some others are missing:
- There's no access using the atalk protocol. I don't have any MAC OS here to test the feature, and anyway newer MAC OS can access SMB shares so I don't think it's a big problem
- There's no FTP access. proftpd is not compiled with mod_facl, and thus, is not compatible with acl
- there's no support for ShadowCopy. I may add this in the future
- You cannot choose a shared folder as the content of a virtual domain. This is because it'd require a modification of a core package
Backup and Restore
The standard backup process should backup all your shared folders. If you have to restore the data to another server, you'll have to re-install the contrib. Once everything is restored, you'll have to run signal-event share-modify-files for each share, because permissions on shared folders uses extended ACL which are not backed up with most tools. This is not a big problem because ACL are also stored in the accounts DB. The signal-event will just re-apply the configured ACL on the files:
for SHARE in $(db accounts printtype | grep share | cut -d'=' -f1); do
signal-event share-modify-files $SHARE
done
Uninstall
If you want to remove the contrib, just run:
yum remove smeserver-shared-folders
You need to manually removes files in /home/e-smith/files/shares if you want to remove every shares created. You may also want to edit /etc/fstab to remove the acl option.
Source
The source for this contrib can be found in the smeserver CVS on sourceforge.
Bugs
Please raise bugs under the SME-Contribs section in bugzilla and select the smeserver-shared-folders component or use this link